
|
Ornithology Bird Biogeography II |
Tropical rain forests (areas that receive more than 100 mm of rain/month) support the richest avifaunas in the world. Why are there so many bird species in rain forests & how (& why) do the avifaunas of rain forests in different parts of the world vary? To answer these questions requires a look at the history of rain forests & their avifaunas (Karr 1990):



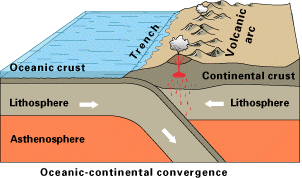
Off the coast of South America, the oceanic Nazca Plate is pushing into & being subducted under the continental part of the South American Plate. In turn, the overriding South American Plate is being lifted up, creating the Andes mountains. |

The convergence of the Nazca and South American Plates has deformed and pushed up limestone strata to form the towering peaks of the Andes, as seen here in Peru /center> |
Tectonic plate collision
Peru High Andes birding
| Avian species richness -- Numerous hypotheses
have been proposed to explain regional variability in species richness,
and recent research efforts have winnowed the number of potential hypotheses
to a credible few: (1) energy availability, (2) evolutionary time, (3)
habitat heterogeneity, (4) area, and (5) geometric constraints. Rahbek
and Graves (2001) examined bird diversity in South America and found
that the 1° quadrats (map a to the right) that exhibited the highest
avian diversity (>650 species) were restricted to Andean Ecuador (peaking
at 845 species) and in southeastern Peru (peaking at 782 species) and southern
Bolivia (peaking at 698 species). These quadrats were physiographically
complex (range = 1,700-5,700 m) and characterized by moderate precipitation
(1,058-3,096 mm/yr) and maximum daily temperatures (16.9-25.3°C). Thus,
neither area nor energy alone is sufficient to explain patterns of avian
species richness in South America. If energy and biome area were the primary
determinants of species richness, then species richness would be highest
in central Amazonia, which was not the case.
Species richness in neotropical birds seems to be linked directly to habitat diversity, which is correlated with topographic heterogeneity. The number of different ecosystems found in 1° quadrats was correlated with topographic relief at tropical latitudes (<20°). Quadrats in the species-poor zone in central Amazonia overlapped 5-16 distinctive ecosystems, whereas species-rich quadrats (>650 species) overlapped 16-24 ecosystems. The extraordinary abundance of species associated with humid montane regions at equatorial latitudes reflects the overwhelming influence of orography and climate on the generation and maintenance of species richness. Rahbek and Graves' (2001) data reinforce the hypothesis that terrestrial species richness from the equator to the poles is governed by a synergism between climate and coarse-scale topographic heterogeneity. |
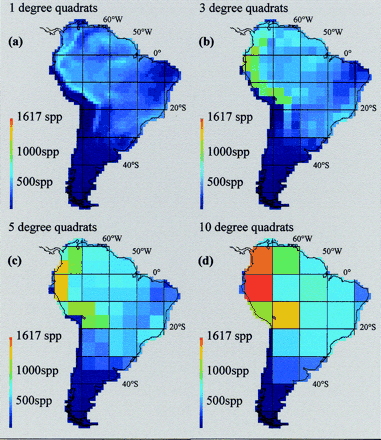
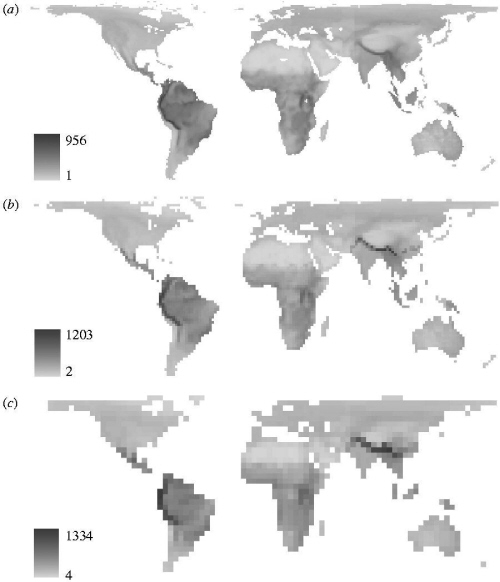
water birds (Aves) of South America compiled at 1° × 1°, 3° × 3°, 5° × 5°, and 10° × 10° scales. Note the loss of information and the spurious extrapolation of high species densities in species-poor localities at coarser spatial scales (From: Rahbek & Graves 2001). |
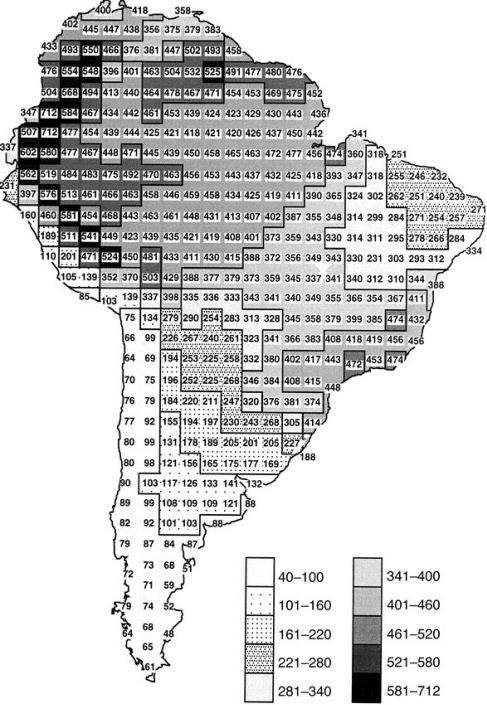
Geographic variation in the richness of breeding terrestrial bird species in South America (Hawkins et al. 2003).
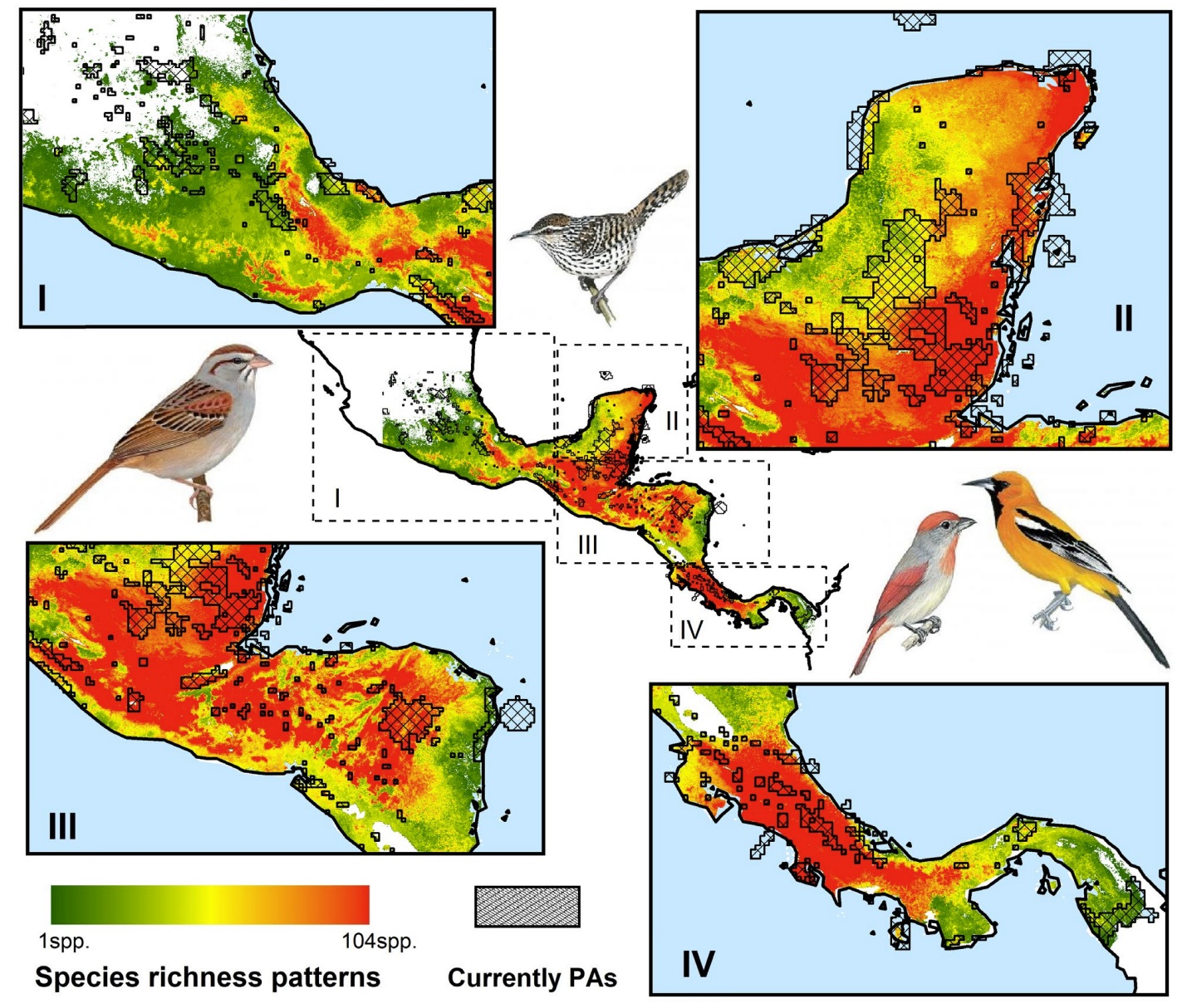
Species richness distribution patterns of 182 endemic bird species in Mesoamerica, and the locations of current
protected areas. About 13%
of Mesoamerican terrestrial surface is covered by designed protected areas (PAs). Birds (from left to right) in maps are
Cinnamon-tailed Sparrow
(Peucaea sumichrasti), Yucatan Wren (Campylorhynchus yucatanicus), Rose-throated Tanager (Piranga roseogularis), and
Orange Oriole (Icterus auratus) (From: Ramírez-Albores et al. 2021).
Mesoamerica is considered among the most important high species richness sites for conservation across the Americas. This biologically complex region extends from central Mexico to southern Panama and northern Colombia. It is mainly composed of highly fragmented tropical forest patches that vary in
size and extent. Mesoamerica has wide topographic and climatic variability and a complex biogeographical history, all of which have promoted important biotic interchange events and extensive diversification in situ due to climatic changes and geological processes. Ramírez-Albores et al. (2021) found that species richness patterns for endemic birds across Mesoamerica tended to be highest in areas considered boundaries between highly biodiverse ecosystems,
such as tropical dry forests and cloud forests throughout Mexico,
Guatemala, Costa Rica and Panama. In contrast, low species richness values were found along the coast and the Caribbean slope. Ramírez-Albores et al. also found that the current PA network is poorly representative of the distributional ranges of endemic bird species in Mesoamerica and does not efficiently cover the conservation needs. For
the conservation of bird diversity and endemism in Mesoamerica, the area encompassed by PAs needs
to be increased, especially in areas with moist forests which is the
the least protected biome across the region.
Global maps of avian species richness at three sampling resolutions. An equal-area (Behrmann) map projection was used,
with grid cells having longitudinal cell resolutions of: (a) 1°; (b) 2° and (c) 4°.
Topography, energy and the global distribution of bird species richness -- A major goal of ecology is to determine the causes of the latitudinal gradient in global distribution of species richness. Current evidence points to either energy availability or habitat heterogeneity as the most likely environmental drivers in terrestrial systems, but their relative importance is controversial in the absence of analyses of global (rather than continental or regional) extent. Davies et al. (2007) used data on the global distribution of extant continental and continental island bird species to test the explanatory power of energy availability and habitat heterogeneity while simultaneously addressing issues of spatial resolution, spatial autocorrelation, geometric constraints upon species' range dynamics, and the impact of human populations and historical glacial ice-cover. Global maps of avian species richness data used in their analyses showed a consistent pattern across all three sampling resolutions (see Figure above), namely higher species richness within the tropics, with peaks coinciding with major mountain chains, most notably along the Andes and the southern slopes of the Himalayas and to a lesser extent the African Rift Valley. The best-fit multi-predictor global model accounting for glacial history and human impacts showed elevation range to be the strongest predictor of avian species richness, closely followed by temperature and then habitat diversity and productive energy. This global perspective confirms the primary importance of mountain ranges in high-energy areas.
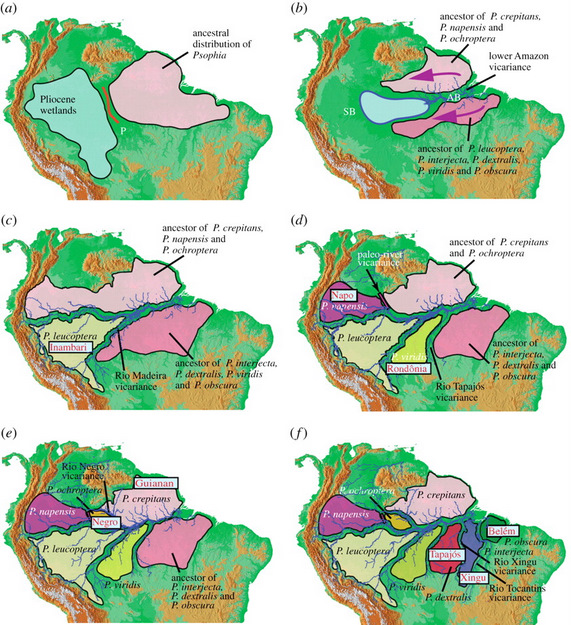
A palaeobiogeographic model for terrestrial environments of Amazonia for the last 3 million years based on the evolutionary history of trumpeters (Psophia) and geological data. Rivers and their tributaries are depicted as in the present, but their palaeopositions may have differed. (a) About 3.0–2.7 million years ago (Ma): western lowland Amazonia is a large interconnected wetland/lake/river system. (b) About 2.7–2.0 Ma: the wetland system drained significantly and the lower Amazon River, which isolated northern and southern populations of Psophia, was established. As terra firme forests developed, populations expanded westward. (c) About 2.0–1.0 Ma: the Rio Madeira drainage was established, promoting speciation of P. leucoptera (Inambari area). (d) About 1.3–0.8 Ma: the Rio Tapajós drainage system developed, resulting in the differentiation of P. viridis (Rondônia area). At the same time, a barrier (red bar) is postulated to have isolated the Napo area of endemism within which P. napensis differentiated. (e) About 1.0–0.7 Ma: an isolating barrier associated with the lower Rio Negro formed, giving rise to P. ochroptera (Negro area) and P. crepitans (Guianan area). (f) About 0.8–0.3 Ma: two drainage systems on the Brazilian Shield, the Rio Tocantins and the Rio Xingu, were established as isolating barriers, creating three areas of endemism and their endemic species. AB, Amazon Basin; SB, Solimões Basin; P, location of Purus Arch.
River dynamics and Amazonia biodiversity -- Many hypotheses have been proposed to explain high species diversity in Amazonia, but few generalizations have emerged. In part, this has arisen from the scarcity of rigorous tests for mechanisms promoting speciation, and from major uncertainties about palaeogeographic events and their spatial and temporal associations with diversification. Ribas et al. (2012) examined the environmental history of Amazonia using a phylogenetic and biogeographic analysis of trumpeters (Aves: Psophia), which are represented by species in each of the vertebrate areas of endemism. Their relationships reveal an unforeseen ‘complete’ time-slice of Amazonian diversification over the past 3 million years. A temporally calibrated phylogeny was employed to test competing palaeogeographic hypotheses. Results were consistent with the establishment of the current Amazonian drainage system at approximately 3.0–2.0 million years ago and predict the temporal pattern of major river formation over Plio-Pleistocene times. Ribas et al. (2011) propose a palaeobiogeographic model for the last 3.0 Myr of Amazonian history that has implications for understanding patterns of endemism, the temporal history of Amazonian diversification and mechanisms promoting speciation. The history of Psophia, in combination with new geological evidence, provides the strongest direct evidence supporting a role for river dynamics in Amazonian diversification, and the absence of such a role for glacial climate cycles and refugia.
As a result of this history (& other factors described below):
Amazon Rainforest deforestation
Birds of the Amazon rainforest

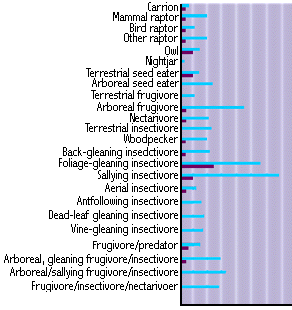
Bird guilds and ecological specialization
(light bars for the tropics, dark bars for the temperate zone)
Source: www.globalchange.umich.edu/globalchange1/current/lectures/kling/rainforest/rainforest.html
| Arboreal dead-leaf-searching birds of the Neotropics -- Remsen and Parker (1984) reported that at least 11 species of birds in northern Bolivia and southern Peru are dead-leaf-searching “specialists”: more than 75% of their foraging observations of these species involved individuals searching for insects in dead, curled leaves suspended above ground in the vegetation. All known specialists of this kind belong to the families Furnariidae and Formicariidae. An additional six species exhibited dead-leaf-searching behavior in 25% to 75% of their foraging records. The number of specialists and regular users decreases with rising elevation in the Andes. Specialists disappear from the gradient between 2,000 m and 2,575 m, but regular users occur as high as 3,300 m, near timberline. As many as eight species of dead-leaf-searching specialists coexist in western Amazonia. |

Photo by Arthur Grosset |
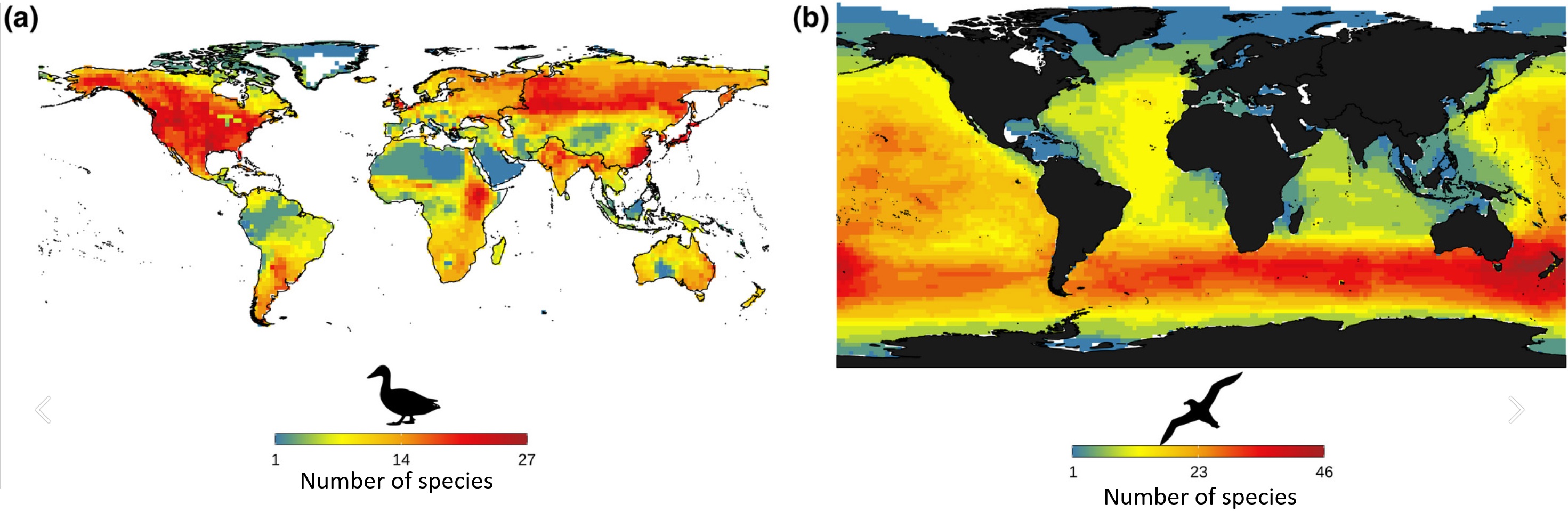
Global species richness map for (a) Anseriformes (ducks and geese); (b) Procellariiformes (petrels and albatrosses). Species richness of
Anseriformes peakes in the Nearctic and Palaearctic regionsm, whereas species richness for Procellariformes peaks in the southern cold
oceans. These taxa probably originated in temperate regions, where their richness currently peaks, suggesting possible synergy between
fast diversification and evolutionary time for species accumulation (From: Cerezer et al. 2022).
Why, in general (i.e., with some exceptions such as Anseriformes [ducks and geese] and Procellariiformes [petrels and albatrosses]), does bird species diversity increase from the poles
to the equator?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
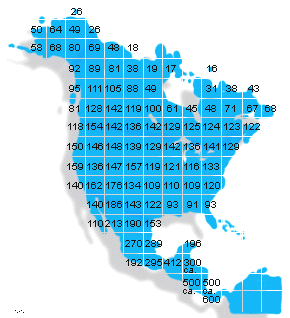
Breeding bird species in North and Central America
Source: www.globalchange.umich.edu/globalchange1/current/lectures/kling/rainforest/rainforest.html
A number of possible explanations for these latitudinal diversity gradients have been suggested (Wiens 1991):
| Tropical Conservatism Hypothesis
-- Wiens and Donoghue (2004) have proposed a 'tropical conservatism hypothesis'
to help explain the the tendency for species richness to increase from
poles to equator. This hypothesis or model combines three basic ideas:
• Many groups of organism that have high tropical species richness originated in the tropics & have spread to temperate regions either more recently or not at all. If a clade originated in the tropics then (all other things being equal) it should have more tropical species because of the greater time available for speciation in tropical regions to occur (i.e. the time-for-speciation effect). • One reason that many extant clades of organism originated in the tropics is that tropical regions had a greater geographical extent until relatively recently (30–40 million years ago, when temperate zones increased in size). If much of the world was tropical for a long period before the present, then (all other things being equal) more extant clades should have originated in the tropics than in temperate regions. • Many species and clades are specialized for tropical climates, and the adaptations necessary to invade and persist in regions that experience freezing temperatures have evolved in only some. Tropical niche conservatism has helped maintain the disparity in species richness over time. At least two lines of evidence support this tropical conservatism hypothesis. First, many groups of organisms that show the expected gradient in species richness also appear to show the predicted pattern of historical biogeography, with an origin in the tropics and more recent dispersal to temperate regions. For example, analyses of New World birds reveal older average divergences among tropical taxa than among temperate ones, as predicted by this hypothesis. Second, many distantly related groups show similar northern range limits, in spite of the lack of an obvious geographical barrier, suggesting that cold climate and niche conservatism act as barriers to the invasion of temperate zones by tropical clades. Thus, many neotropical clades currently have their northern range limits in the tropical lowlands of Mexico (e.g., tinamous), whereas many other groups have their northern range limits in southern China and Vietnam (e.g., broadbills). These regions of biotic turnover in Mexico and Asia have not gone unnoticed; in fact, they correspond to borders between the global zoogeographical realms recognized by Wallace. Further, many of the groups involved are old, suggesting that there has been ample time for invasion of temperate regions, but that their northward dispersion was limited by their inability to adapt to colder climates. |
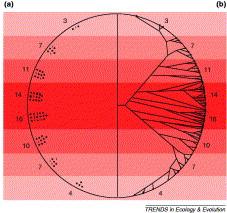 Two approaches to the problem of explaining global patterns of species richness. Standard ecological approaches (a) seek correlations between the numbers of species of a given group at a given location (numbers along the edge of the globe) & environmental variables (e.g., temperature, indicated here by different shades
of red). By contrast (b), Wiens & Donoghue (2004) advocate considering the biogeographical history of the species and clades that makes up these differences in species richness between regions, & understanding how ecology, phylogeny & microevolution (e.g. adaptation) have combined to shape that biogeographical history. Each dot in the above diagram represents a species & its geographical location, and the lines connecting
them represent both their evolutionary relationships and the simplified paths of dispersal. (b) also illustrates the tropical conservatism hypothesis, i.e., there are more
species in tropical regions because most groups originated in the tropics & are specialized for a
tropical climatic regime, that most species and clades have been unable to disperse out of the tropics (because of niche conservatism), and that the greater time and area available or speciation in the tropics has led to higher species richness in the tropics for most taxa. As shown here, the tropical conservatism hypothesis predicts that temperate lineages are often recently derived from clades in tropical regions, leading to (on average) shallower phylogenetic divergences among temperate lineages than among tropical lineages. Although not illustrated here, an important part of the tropical conservatism hypothesis is the idea that tropical regions were more extensive until the mid-Tertiary, which might help explain the greater number of extant clades originating in these areas. |
Some terrestrial birds can be found almost everywhere. For example, Ospreys, Barn Owls, & swifts occupy every continent except Antarctica. However, although most can fly, most species of birds do not occur everywhere on earth where conditions appear to be favorable for them. Barriers to dispersal for birds include (Welty & Baptista 1988):

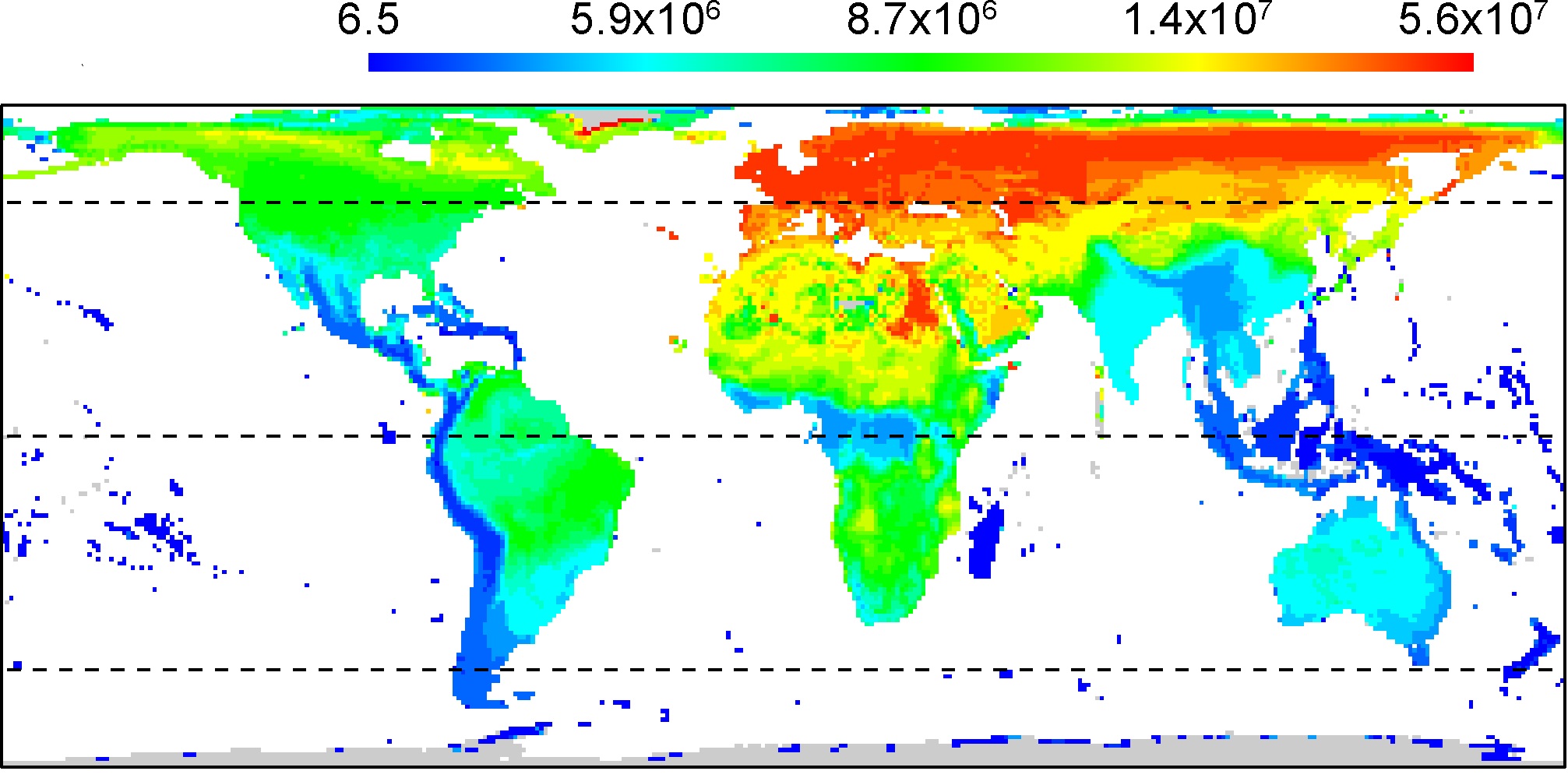
Median geographic range area (km2) of birds. Most species have small, but not the smallest, geographic ranges. Overall,
birds with smaller ranges are
found on islands, mountainous areas, and in the southern hemisphere. In addition, median
range area and species richness were found to be
significantly negatively related. Smaller geographic ranges on islands and in
mountain ranges in
the tropics
and subtropics suggest that range areas may be constrained by the availability of land area in
the climatic zones to which species are best adapted. Finally, although analysis revealed a significant negative association
between range area and species richness, the strength of that relationship was not strong. For those analyses based on
non-spatial models, the maximum proportion of variance explained was only 18%. As a result, it would be wrong to
conclude that smaller range areas are strongly associated with higher levels of species richness, although there is robust
evidence that the two variables are not entirely independent, both globally and within some biogeographic realms. It remains to
be determined if global patterns in geographic range size are best interpreted in terms of geographical variation in species assemblage
packing, or in the rates of speciation, extinction, and dispersal that ultimately underlie biodiversity (From: Orme et al. 2006).
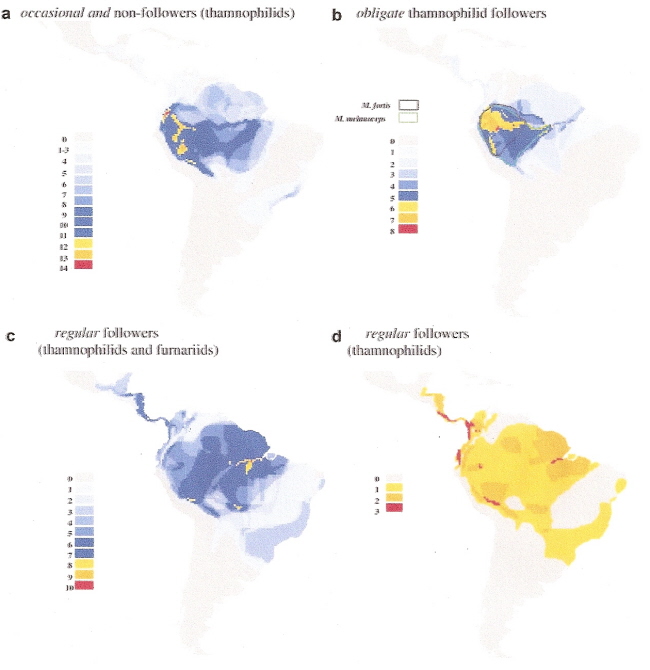
Species-richness maps of (a) occasional/non-following species that are sister to ant-following clades, (b) obligate
army-ant-followers [with distributions of Myrmeciza fortis (obligate) and M. melanoceps (occasional) outlined],
(c) regular army-ant-followers (thamnophilid and furnariid species combined), and (d) regular thamnophilid army-ant-followers.
Army-ant-following birds -- One of the most novel foraging strategies in Neotropical birds is army-ant-following, in which birds prey upon arthropods and small vertebrates flushed from the forest floor by swarm raids of the army-ant Eciton burchellii. This specialization is most developed in the typical antbirds (Thamnophilidae) which are divisible into three specialization categories: (1) those that forage at swarms opportunistically as army-ants move through their territories (occasional followers), (2) those that follow swarms beyond their territories but also forage independently of swarms (regular followers), and (3) those that appear incapable of foraging independently of swarms (obligate followers). Brumfield et al. (2007) found that regular following evolved only three times, and that the most likely evolutionary progression was from least (occasional) to more (regular) to most (obligate) specialized, with no reversals from the obligate state. Despite the dependence of the specialists on a single ant species, molecular dating indicates that army-ant-following has persisted in antbirds since the late Miocene.
Ant-following species density maps (above) illustrate clear differences between obligate and regular followers. Obligate followers are found almost exclusively in Amazonia, with increasing densities moving west toward the Andes. This same pattern is observed in occasional/non-followers. In contrast, regular followers were most abundant where obligates were least prevalent or absent (Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil, the Guyanan shield, and the forested lowlands west of the Andes). These results suggest that competition could have played a role in the evolution of army-ant-following species and in shaping their distribution.
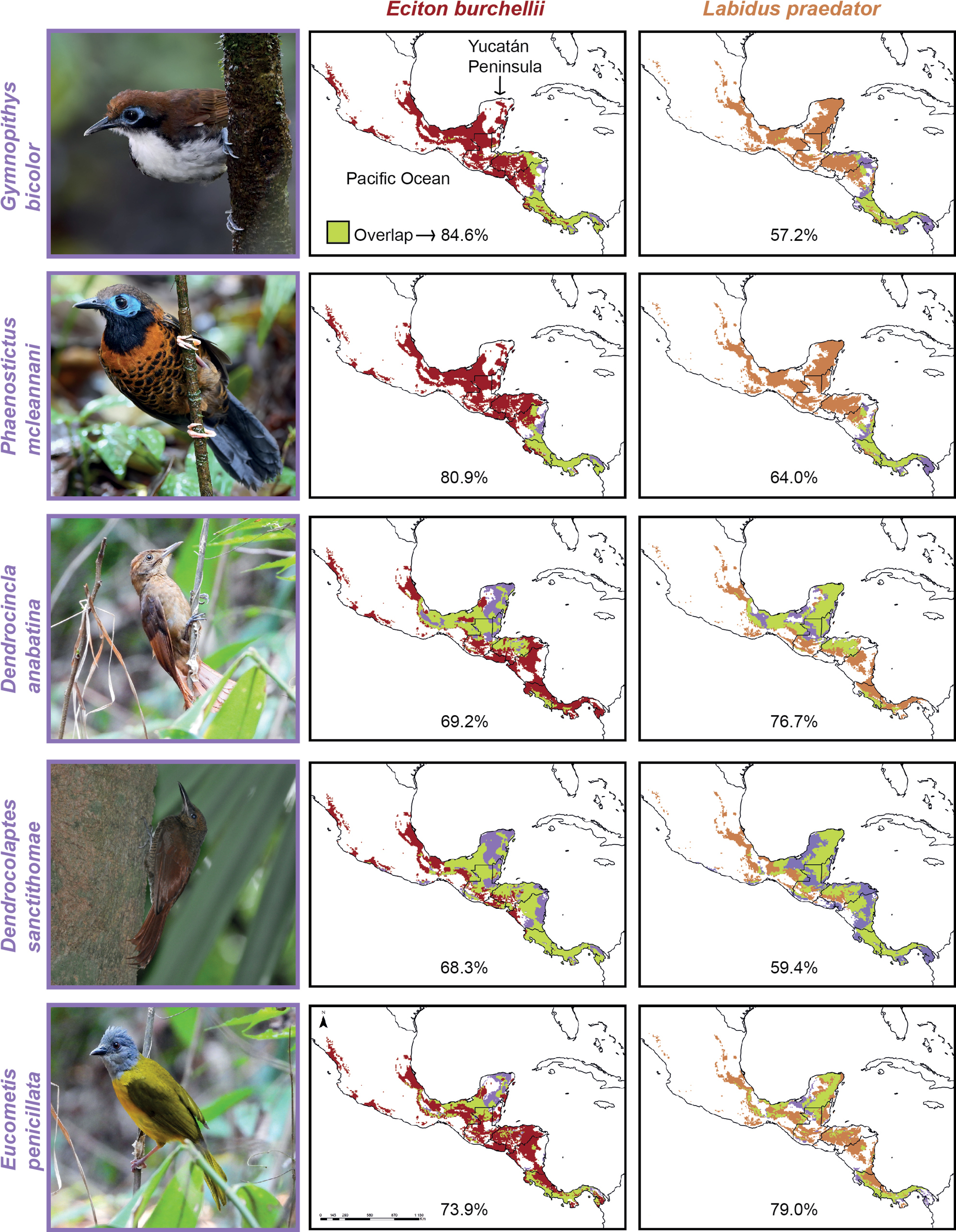
Overlap of species distribution models of two species of army ants (columns;
Eciton burchellii, carmine color, and
Labidus
pra
edator
, caramel color) and five species of obligate ant-following birds (rows, amethyst color) in Mexico and Central America. Range
overlap between army ants and ant-following birds is shown in lime color, and the percentage of overlap is represented numerically for each
ant-bird species pair (From:
Interiano et al. 2024).
Migration & Bird Biogeography
The avifauna of most regions (Nearctic, Palearctic, Neotropical, Ethiopian, & Oriental) includes numerous migratory species; species that spend only part of the year in those regions. About 400 species have breeding ranges in the Holarctic and winter in the tropics (primarily Central & South America, Africa, & Indomalaysia)(Lovei 1989).
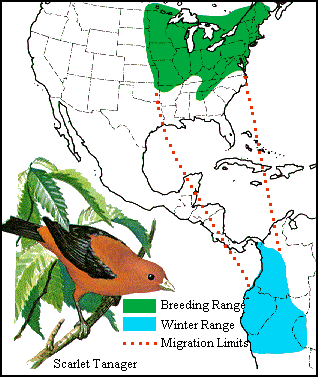
What is the ancestral 'home' of migrants? For example, are most migrants in this hemisphere Nearctic species that move south to avoid winter conditions or Neotropical species that move north to take advantage of temporarily favorable conditions for breeding? Evidence suggests that many northern latitude migrants are tropical birds exploiting the long days and abundant insects of high-latitude summers rather than temperate birds escaping northern winters (Levey and Stiles 1992).
Migration Flyways
Flyways
Bird migration
Reconstructing the geographic and climatic origins of long-distance bird migrations
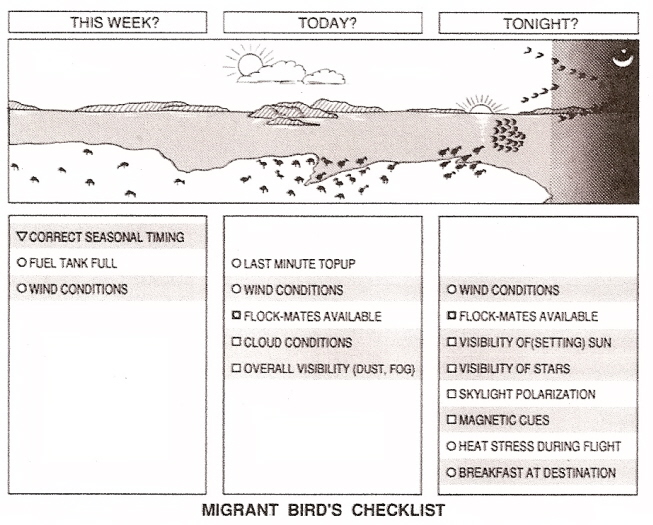
Checklist of things a migrant bird has to consider before departing on a long-distance flight (Piersma et al. 1990, Klaasen 1996).
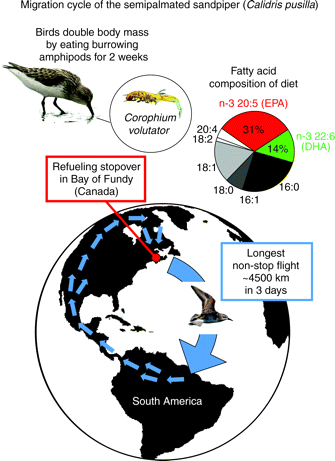 |
Semipalmated Sandpipers (Calidris pusilla) stop in the Bay of Fundy (New Brunswick, Canada) during their fall migration from breeding areas in the Arctic. This crucial stopover allows the sandpipers to store large lipid reserves by eating seasonally abundant amphipods (Corophium volutator) buried in the mudflats. An estimated 75% (about 1 million individuals) of the world population of Semipalmated Sandpipers stops at this location. The Corophium mudshrimp contains unusually large amounts of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty aids (45% of total lipids) and is found only in the Bay of Fundy and along the coast of Maine. Dietary n-3 fatty acids are not only used as an energy source, but they also act as performance-enhancing substances to increase the capacity for endurance exercise, just before the sandpipers cross the Atlantic ocean to South America. The remainder of the annual migration cycle appears to be achieved through multiple short flights over land and along coastal areas. Pollution and rising sea levels caused by global warming are major threats to strategic stopover sites such as the Bay of Fundy and to the future of these sandpipers (Weber 2009). |
Semipalamated Sandpipers
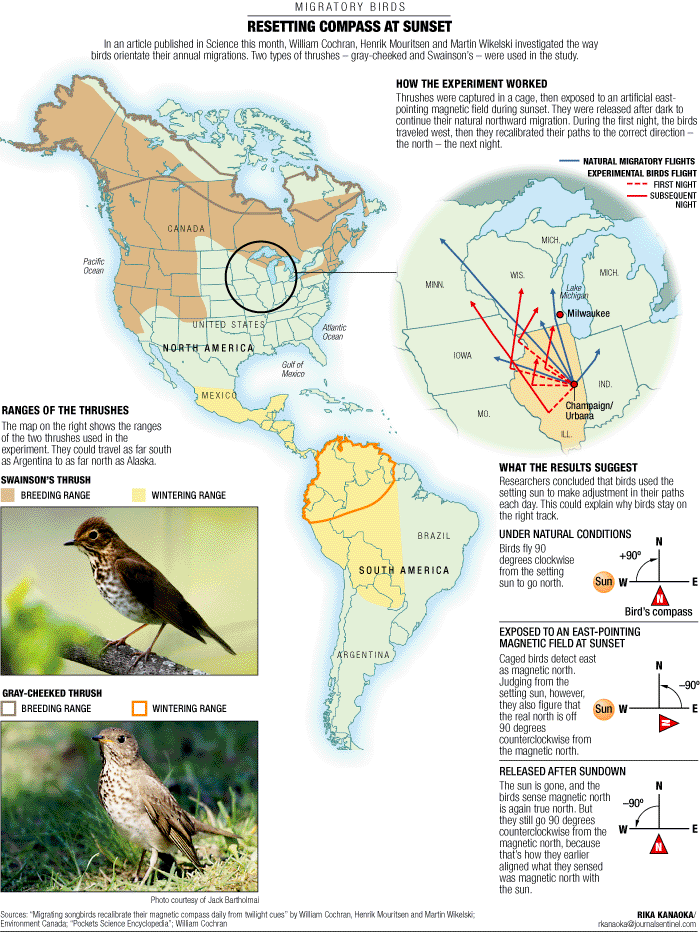
Sense of direction -- Cochran et al. (2004) found that migrating thrushes rely on a built-in magnetic compass that they recalibrate each evening based on the direction of the setting sun. The research, that involved attaching radio transmitters to birds and following them by truck is the first extensive study of bird navigation in the wild. The results appear to resolve conflicts between earlier laboratory-based studies, which had identified several possible navigational mechanisms, but produced no consensus. Previous theories suggested that birds use some combination of magnetism, stars, landmarks, smells and other mechanisms as navigational aides. Cochran et al. (2004) caught birds just before they left for their overnight migratory flights and placed them in an artificial magnetic field. They then released the birds and followed them throughout the night. Birds that had been in the artificial magnetic field flew in the wrong direction, but recovered their orientation the next night.
"In the morning, shortly before they land, they see the sun and realize they have made a mistake," said Martin Wikelski, a co-author. "You can see them turn around 90 degrees." Cochran et al. (2004) concluded that birds rely on the location of the sunset to determine which way to fly. To maintain that heading throughout the night, they sense the Earth's magnetic field, just like a pilot uses a compass at night or in bad weather. "It is the simplest and most foolproof orientation mechanism we can imagine," Wikelski said. The combination of cues sun and magnetic field neatly correct each other for possible problems. Migrating at night, birds cannot maintain a fix on the sun and cannot rely on seeing stars because of clouds. A bird's magnetic compass also is not sufficient. The location of the magnetic north pole the spot on the globe where a compass points is not stable (it is currently in Canada, hundreds of miles from the geographic north pole). The magnetic poles also completely reverse locations every few thousand years, so the north arrow on a compass would suddenly point south. It makes sense then that birds use the magnetic field only as a guide to keep them on a path that is determined primarily by the sun, Wikelski said. It doesn't matter which way the magnetic field points, so long as it stays steady through the night.
In one set of experiments, the researchers tracked Gray-cheeked Thrushes, which all tend to migrate in the same direction. Seven of eight birds exposed to an artificial magnetic field flew in a significantly different direction than 14 that were not. The researchers did similar experiments with Swainson's Thrushes (pictured above), whose headings vary considerably from one bird to another. They exposed the Swainson's thrushes to artificial magnetic fields and followed them for at least two days. All the treated birds picked a significantly different direction on their second day, whereas unmanipulated birds kept flying the same direction both days. Wikelski believes the results, while based on just two species, are likely to apply to most migratory birds. "It's such a simple and elegant mechanism that I would say it is widespread," he said. -- Princeton Weekly Bulletin
Bats vs. migrating Palearctic passerines -- Along food chains, i.e., at different trophic levels, the most abundant taxa often represent exceptional food reservoirs, and are hence the main target of consumers and predators. The capacity of an individual consumer to opportunistically switch towards an abundant food source, for instance, a prey that suddenly becomes available in its environment, may offer such strong selective advantages that ecological innovations may appear and spread rapidly. New predator-prey relationships are likely to evolve even faster when a diet switch involves the exploitation of an unsaturated resource for which few or no other species compete. Using stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen as dietary tracers, Popa-Lisseanu et al. (2007) reported support for the controversial hypothesis that the greater noctule bat (Nyctalus lasiopterus), a rare Mediterranean aerial-hawking bat, feeds on the wing upon the multitude of flying passerines during their nocturnal migratory journeys, a resource that, although showing a predictable distribution in space and time, is only seasonally available. No predator had previously been reported to exploit this extraordinarily diverse and abundant food reservoir represented by nocturnally migrating passerines.
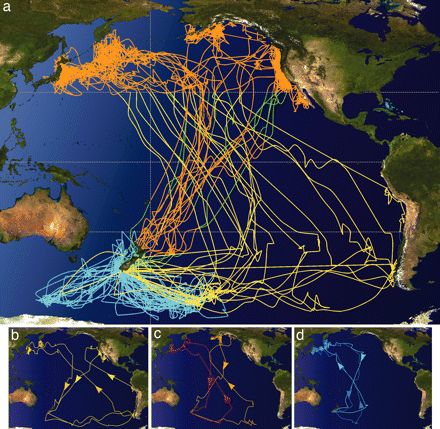
Shearwater migrations originating from breeding colonies in New Zealand. (a) Interpolated geolocation tracks of 19 Sooty Shearwaters
during breeding (light blue) and subsequent migration pathways (yellow, start of migration and northward transit; orange, wintering grounds and
southward transit). The 30° parallels, equator, and international dateline are indicted by dashed lines. (b–d) Representative figure-eight movement
patterns of individual shearwaters traveling to one of three "winter" destinations in the North Pacific. These tracks also represent those of three breeding
pairs to reveal the dispersion and extent of each pair.
Electronic tracking tags have revolutionized our understanding of broad-scale movements and habitat use of highly mobile marine animals, but a large gap in our knowledge still remains for a wide range of small species. Shaffer et al. (2006) reported the extraordinary transequatorial postbreeding migrations of a small seabird, the Sooty Shearwater (Puffinus griseus), obtained with miniature archival tags that log data for estimating position, dive depth, and ambient temperature. Tracks (262 ± 23 days) revealed that shearwaters fly across the entire Pacific Ocean in a figure-eight pattern while traveling 64,037 ± 9,779 km roundtrip, the longest animal migration ever recorded electronically. Each shearwater made a prolonged stopover in one of three discrete regions off Japan, Alaska, or California before returning to New Zealand through a relatively narrow corridor in the central Pacific Ocean. Transit rates as high as 910 ± 186 km·day–1 were recorded, and shearwaters accessed prey resources in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere’s most productive waters from the surface to 68.2 m depth. Their results indicate that Sooty Shearwaters integrate oceanic resources throughout the Pacific Basin on a yearly scale. Sooty Shearwater populations today are declining, and because they operate on a global scale, they may serve as an important indicator of climate change and ocean health.
Recent changes in Bird Biogeography - Extinction:
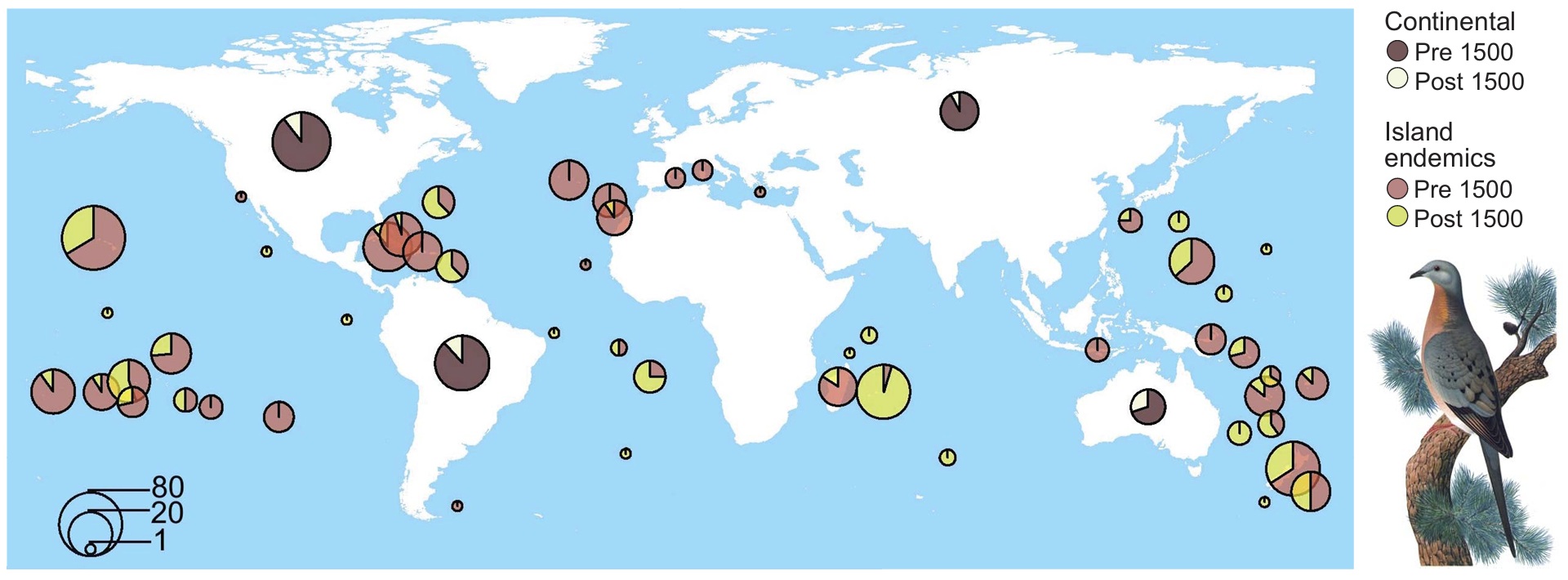
Since the Late Pleistocene, the extinction of 610 bird species has caused a disproportionate loss of the global avian functional space along with ~3 billion years
of unique evolutionary history. For island endemics, proportional losses have been even greater. Projected future extinctions of more than 1000 species over the next two centuries
will incur further substantial reductions in functional and phylogenetic diversity. This figure shows the distribution of extinct bird species, separated into island endemics
and continental species. In each case, the proportion of pre–1500 CE and post–1500 CE extinctions are shown. Some islands were grouped into archipelagos (e.g., Hawaii).
Continental species are organized by realm: Nearctic, Palearctic, Australasia, and Neotropics. The number of extinctions has been logged (with 1 added to each value)
for visual clarity (From: Matthews et al. 2024).
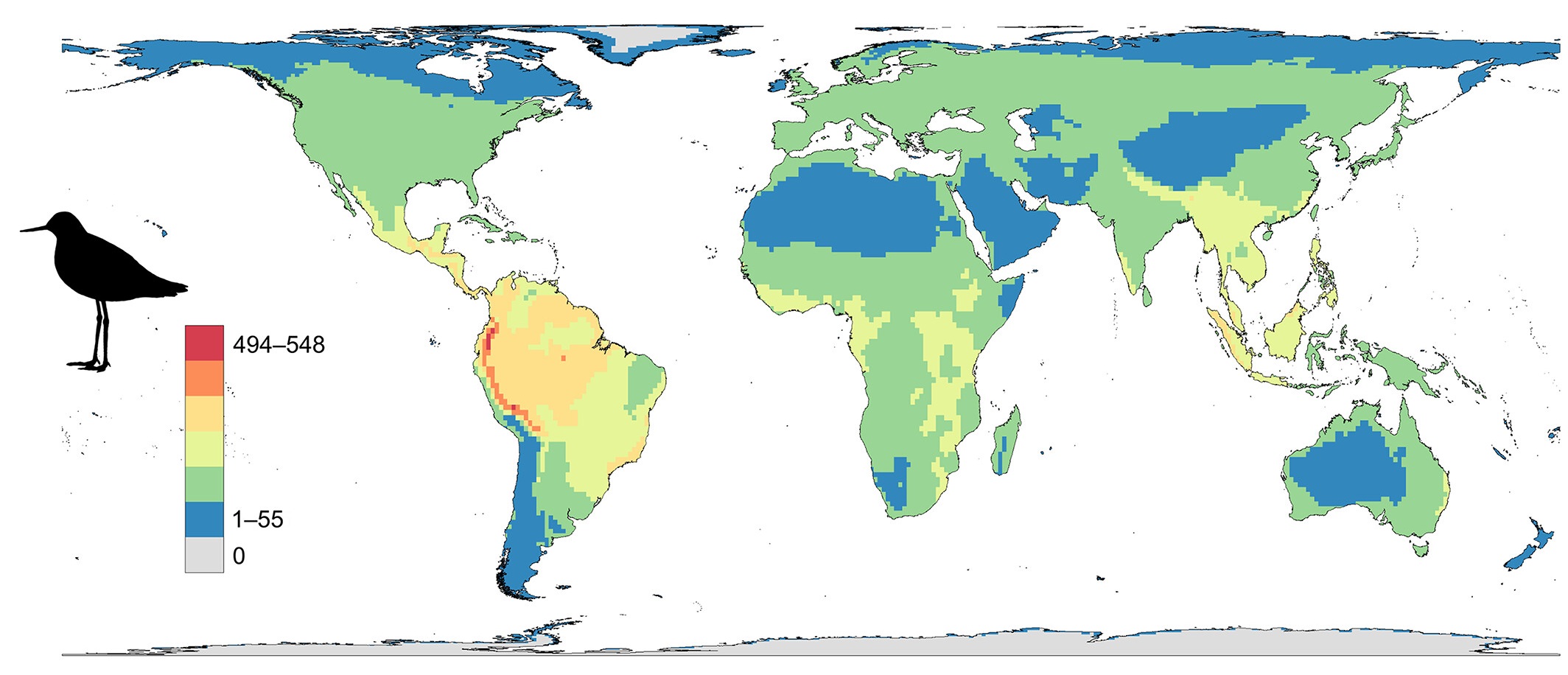
The global distribution of birds with decreasing populations (From: Finn et al. 2023).
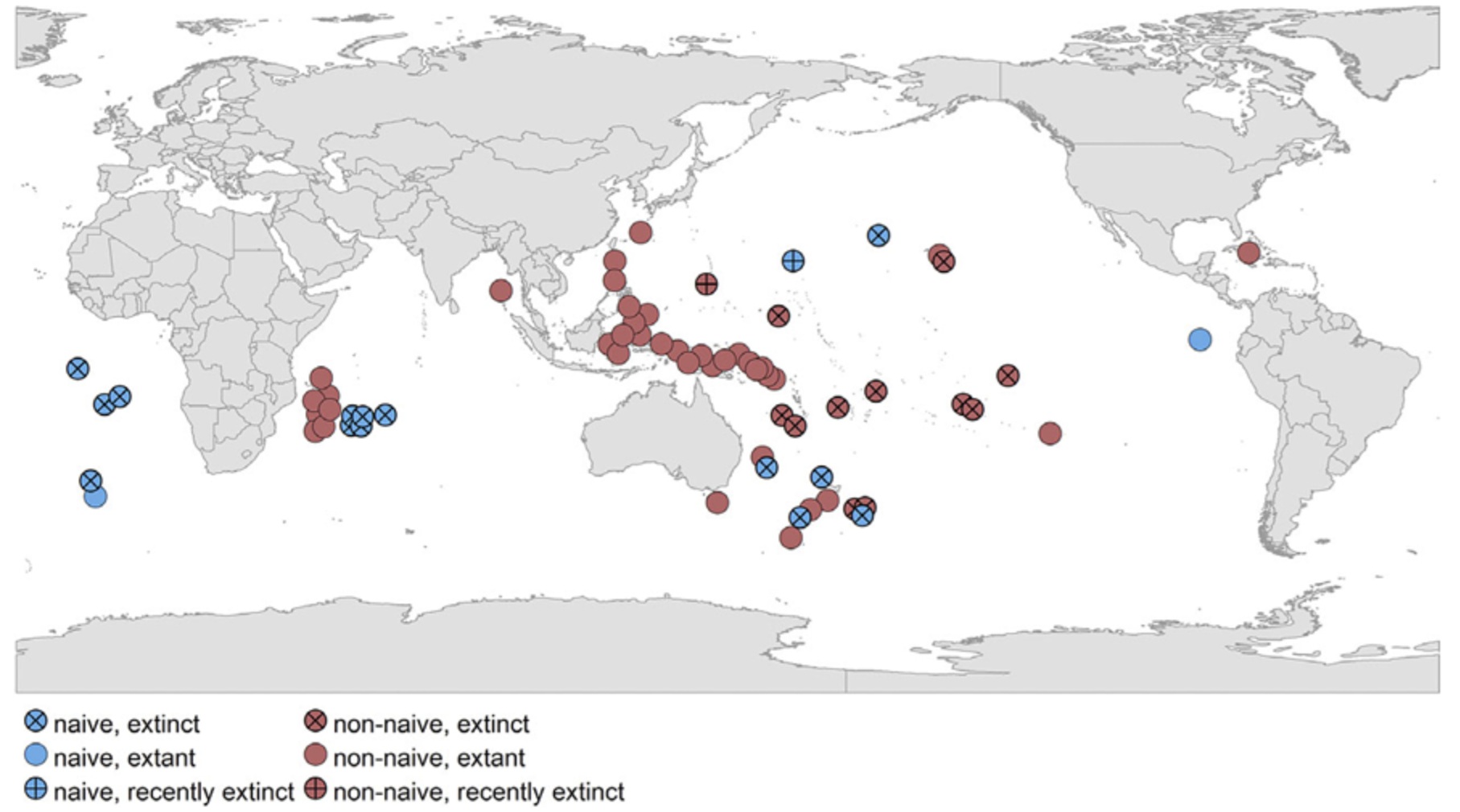
Global distribution of island rails since the Era of Colonialism (i.e., 16th century onwards). Symbols illustrate their fate, i.e., extinct or extant (not extinct)
(cross: extinct, vertical cross: recently extinct, plain: extant). Colors illustrate rails’ state of naivety to humans at the time of contact (blue: naïve, red: not naïve).
Patterns of extinction risk can vary across taxa, with species of some groups being particularly vulnerable to extinction. Rails (Aves: Rallidae) represent one of the most extreme yet well-documented cases of mass extinction within a modern vertebrate group. Between 54 and 92% of rail species became extinct following waves of human contact during both the Holocene and the Anthropocene eras, and a third of the extant species are currently threatened or near-threatened. During the first human initiated extinction wave during the Holocene, all extinct island birds were naturally naïve to people and most of them exhibited no antipredatory behavior because the oceanic islands where they evolved had no mammalian predators. Local studies on island-groups (e.g., Hawaii, New Zealand and Pacific islands) revealed that flightlessness and body size were the main extinction drivers during this first extinction wave. During the most recent wave of extinction, body size was an important correlate of rail extinctions, with both smaller- and larger-bodied species more likely to become extinct. Island endemism and small clutch sizes were the strongest predictors of contemporary vulnerability. Overall, island endemic rails tend to follow the same trajectory as extinct species, suffering most from invasive predators and overhunting (From: Lévêque et al. 2024).
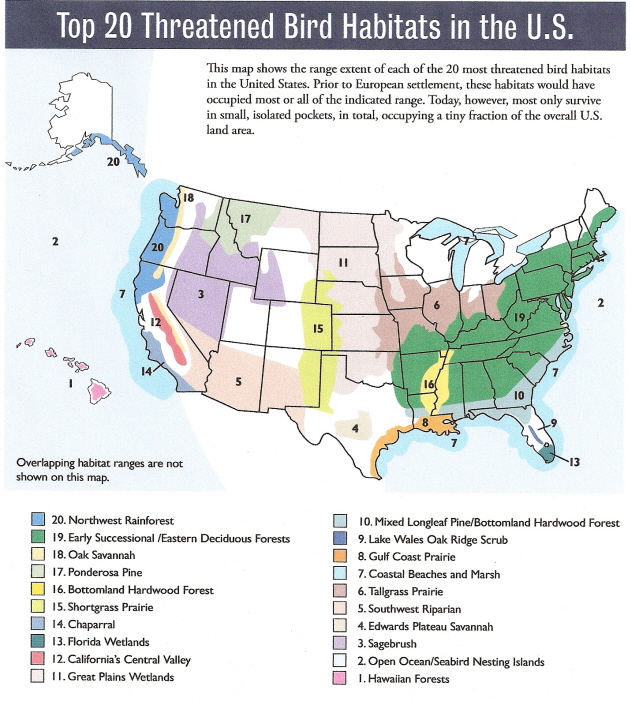
Source: American Bird Conservancy
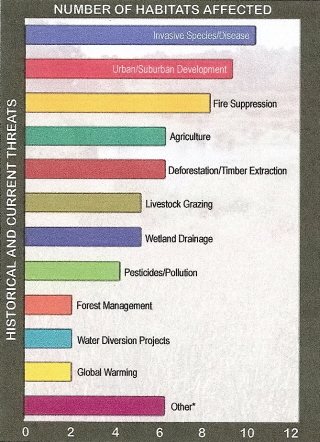
Threats (historical & current) that have been the primary causes of habitat loss in U.S. threatened habitats.
Threats that have only affected one each of the 20 most threatened habitats are combined as 'other',
and include forest succession, coastal engineering, deer, fisheries issues, recreation, and fire
(Source: American Bird Conservancy).
Birds face extinction
Overview of 2.9 billion decline in North American birds since 1970 by Mark Robbins
In October 1993, William Lishman took off from his Toronto farm in a microlight of his own design and construction.
Eighteen birds followed 'Goose Leader' in a V-formation all the way south to Virginia. The following April the banded
flock returned unaided to Lishman's farm to greet their surrogate father. Eventually the principles learned by working
with Canada Geese and Sandhill Cranes were applied to endangered species such as Whooping Cranes and Trumpeter Swans.
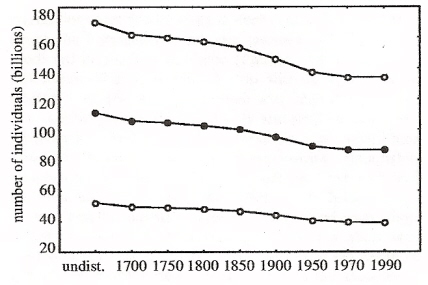
Estimated global numbers of individual birds (in billions) over the past
several hundred years, based on low (bottom), medium (middle), and high (top)
densities, beginning with the pre-agricultural pattern of land use (Gaston et al. 2003).
Habitat conversion and global avian biodiversity loss -- The magnitude of the impacts of human activities on global biodiversity has been documented at several organizational levels. However, although there have been numerous studies of the effects of local-scale changes in land use (e.g. logging) on the abundance of groups of organisms, broader continental or global-scale analyses addressing the same basic issues remain largely wanting. Nonetheless, changing patterns of land use, associated with the appropriation of increasing proportions of net primary productivity by the human population, seem likely not simply to have reduced the diversity of life, but also to have reduced the carrying capacity of the environment in terms of the numbers of other organisms that it can sustain. Gaston et al. (2003) estimated the size of the existing global breeding bird population, and made a first approximation as to how much this has been modified as a consequence of land-use changes wrought by human activities. Summing numbers across different land-use classes gives a best current estimate of a global population of about 87 billion breeding bird individuals (with about 25% of these birds in tropical forest, 13% in tropical woodland, 11% in boreal forest, 8% in savannah habitat, and 19% in human-modified habitats like cropland and pasture). Applying the same methodology to estimates of original land-use distributions suggests that conservatively this may represent a loss of between 20-25% of pre-agricultural bird numbers. This loss is shared across a range of temperate and tropical land-use types.
 |
|
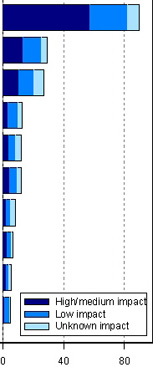
Major threats to globally threatened bird species
(Source: IUCN)
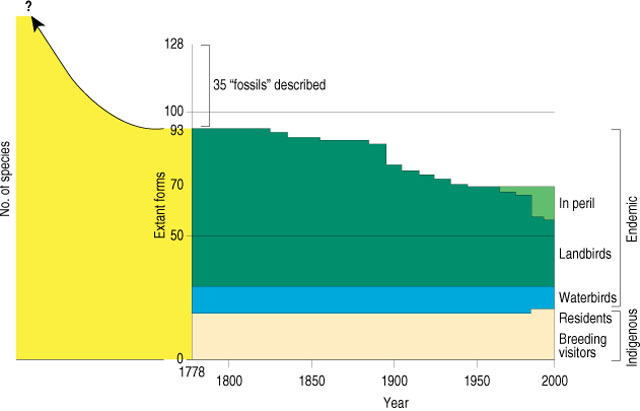
Extinction of native breeding birds since 1778. Steps
mark the decade of the last record for each form considered extinct (A.O.U.
1983).
The 70 forms shown as currently existing include 13 in
peril, with steps marking the decades of their last known records.
Yellow represents prehistoric forms. (Source: biology.usgs.gov/s+t/noframe/t017.htm)
Saving Hawaii forest birds
There were once more than 50 known species of honeycreepers in Hawaii, but today only 17 are left, most of which are endangered. One of the biggest factors in this natural history catastrophe is avian malaria. Neither the single-celled organism that causes malaria, nor the mosquito that transmits it, are native to Hawaii, so honeycreepers and other endemic birds have almost no immunity to it. All conservationists agree that something needs to be done – and quickly – to try and save those that remain. Investigators in Hawaii are currently using drones to drop millions of lab-reared, sterile male mosquitoes to combat avian malaria. These mosquitoes are non-biting, lab-reared males carrying a common bacterium that results in eggs that don’t hatch when the males mate with wild females. The hope is that they will help control Hawaii's invasive mosquito population, which is decimating native bird populations, including the rare Hawaiian honeycreepers.

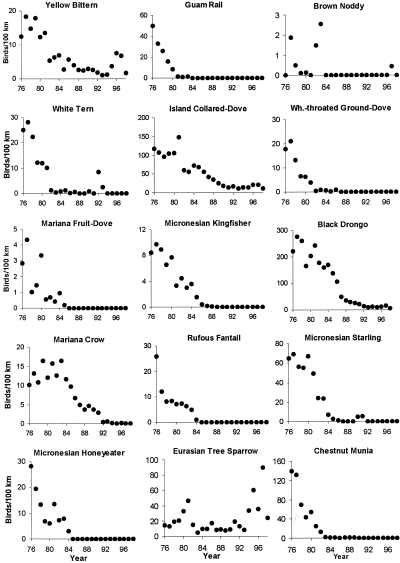
Population trends for Guam birds as indicated by roadside surveys, 1976–1998 (Wiles et al. 2003).
Attenborough And The Giant Egg
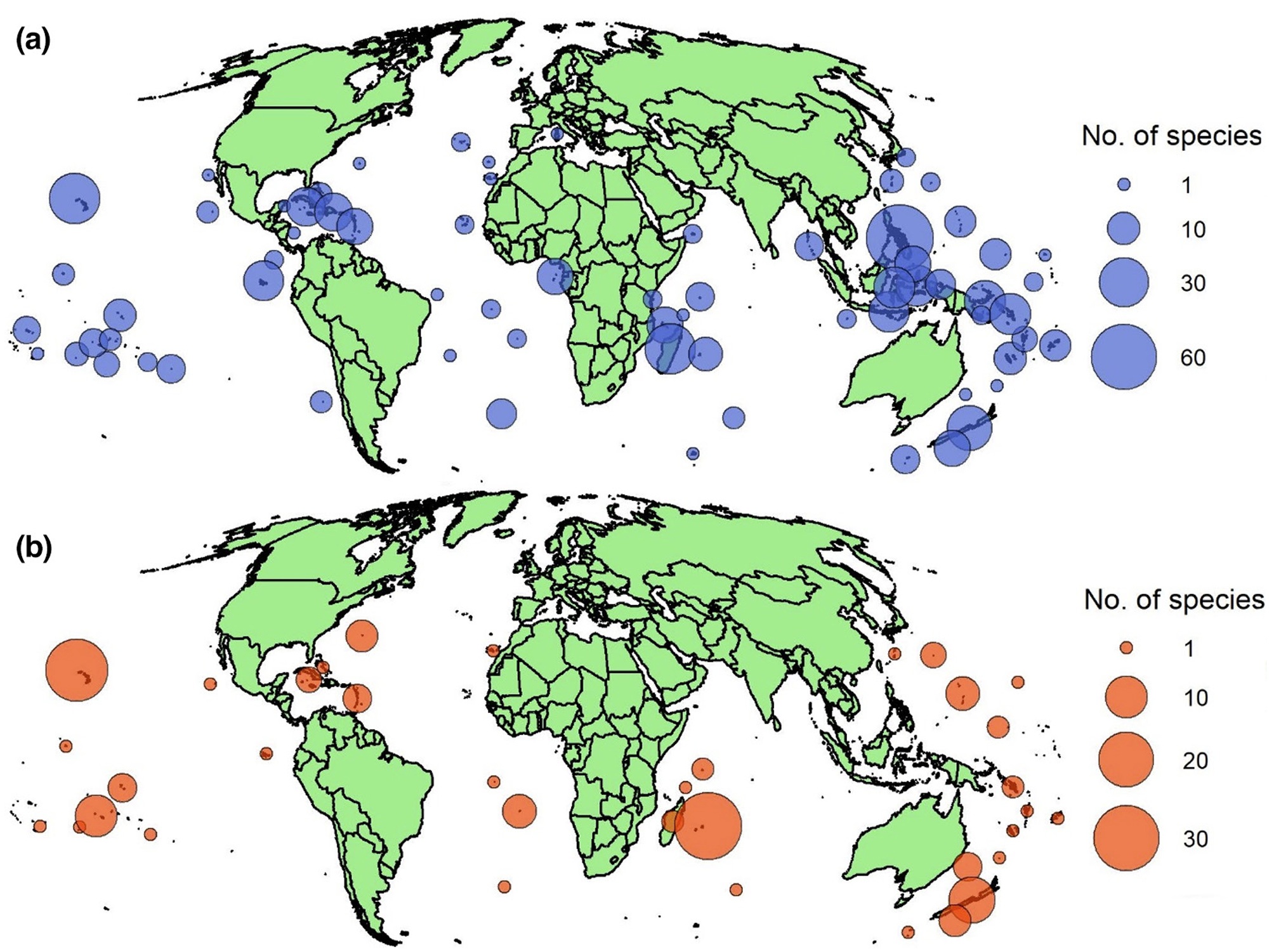
Maps of (a) threatened and (b) extinct island endemic bird species. In (a) all threatened island endemic species
(i.e., those classified as Critically Endangered, Endangered and Vulnerable) are included. Threatened species endemic to
multiple island groups were double counted. Only native ranges (i.e., not introduced ranges) were included, and for
seabirds, only island used for breeding were included. In (b), only species classified as Extinct are included (i.e., species
that went extinct since 1500CE).
Threatened island endemic species are found on a wide range of island groups across the world, but hotspots include the Philippines, several island groups in Indonesia, Madagascar, Hawaii, the Caribbean, New Zealand, and the Bismarck and Solomon archipelagos. Several other Pacific island groups support numerous threatened endemic bird species. A wide range of island groups have also seen species extinctions, with the four most affected being the Mascarene Islands (32 extinctions), the Hawaiian Islands (27), New Zealand (13) and the Society Islands (10). Overall, Polynesia and Melanesia, the Caribbean, East Asian islands and the island groups around Madagascar have all seen large numbers of extinctions.
Almost half of all island endemic birds extant in 1500 CE are currently either extinct or threatened with extinction, with most threatened extant species having declining population trends. The primary threats to extant island endemic birds are agriculture, biological resource use, and invasive species. Traits associated with threatened island endemic birds are large body mass, flightlessness, aquatic predator, omnivorous and vertivorous trophic niches, marine habitat affinity, and, paradoxically, higher dispersal ability. The loss of threatened species may have severe effects on the ecological functions birds provide on islands (From: Matthews et al. 2022).
An endemic radiation of Malagasy songbirds --
The bird fauna of Madagascar includes a high proportion of endemic  species,
particularly among the passerines. The endemic genera of Malagasy songbirds
are not allied obviously with any African or Asiatic taxa, and their affinities
have been debated since the birds first were described. Cibois et al. (2001)
used mitochondrial sequence data to estimate the relationships of 13 species
of endemic Malagasy songbirds, 17 additional songbird species, and one
species of suboscine passerine. Most previous classifications of these
endemic Malagasy songbirds suggested colonization of Madagascar by at least
three different lineages of forest-dwelling birds (babblers,bulbuls, & warblers), but the phylogeny of Cibois et al. (2001) suggests a single
colonization event. They suggest that a single colonization seems more
likely, based on the observation that successful colonization of islands
by forest-restricted birds is rare. The avifauna of islands typically is
comprised of habitat generalists, while nine species in the endemic Malagasy
clade are forest dwelling. Overall, the endemic Malagasy songbird clade
rivals other island radiations, including the vangas of Madagascar and
the finches of the Galapagos, in ecological diversity. species,
particularly among the passerines. The endemic genera of Malagasy songbirds
are not allied obviously with any African or Asiatic taxa, and their affinities
have been debated since the birds first were described. Cibois et al. (2001)
used mitochondrial sequence data to estimate the relationships of 13 species
of endemic Malagasy songbirds, 17 additional songbird species, and one
species of suboscine passerine. Most previous classifications of these
endemic Malagasy songbirds suggested colonization of Madagascar by at least
three different lineages of forest-dwelling birds (babblers,bulbuls, & warblers), but the phylogeny of Cibois et al. (2001) suggests a single
colonization event. They suggest that a single colonization seems more
likely, based on the observation that successful colonization of islands
by forest-restricted birds is rare. The avifauna of islands typically is
comprised of habitat generalists, while nine species in the endemic Malagasy
clade are forest dwelling. Overall, the endemic Malagasy songbird clade
rivals other island radiations, including the vangas of Madagascar and
the finches of the Galapagos, in ecological diversity. |
Why have so many endemic species been lost from islands? The main problems arise from exotic (introduced, non-native) plants, predators and herbivores. They have caused island extinctions in the following ways:
 Howe
and the South Cape Island. On the Galapagos islands, black rats have reduced
populations of the Dark-rumped
Petrel by preying on eggs. Some islands have received introduced rats
without consequent extinction waves. These include Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa.
These are islands that have native rats or land crabs. Land crabs are nocturnal
scavengers that climb trees, enter holes and are the invertebrate ecological
equivalent of rats. Presumably, species that have evolved along with land
crabs are well adapted to defend themselves against rats.
Howe
and the South Cape Island. On the Galapagos islands, black rats have reduced
populations of the Dark-rumped
Petrel by preying on eggs. Some islands have received introduced rats
without consequent extinction waves. These include Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa.
These are islands that have native rats or land crabs. Land crabs are nocturnal
scavengers that climb trees, enter holes and are the invertebrate ecological
equivalent of rats. Presumably, species that have evolved along with land
crabs are well adapted to defend themselves against rats.
| Stephens Island Wren (Traversia lyalli) is only known from recent times from Stephen's Island, New Zealand, although it is common in fossil deposits from both of the main islands. The species was flightless and restricted to the rocky ground. Construction of a lighthouse on Stephens Island in 1894 led to the clearance of most of the island's forest, with predation by the lighthouse keeper's cat delivering the species' coup-de-grace. |

Source: www.nzbirds.com/StephensWren.html |
Easter Island
For birds, Easter Island’s remoteness and lack of predators made it an ideal haven as a breeding site, at least until humans arrived. Among the prodigious numbers of seabirds that bred there were albatross, boobies, frigate birds, fulmars, petrels, prions, shearwaters, storm petrels, terns, and tropic birds. With at least 25 nesting species, Easter Island was the richest seabird breeding site in Polynesia and probably in the whole Pacific. Pollen records show that destruction of Easter Island’s forests was well under way by the year 800, just a few centuries after the start of human settlement. Not long after 1400, the palm became extinct, and soon thereafter the forest itself. Its doom had been approaching as people cleared land to plant gardens; as they felled trees to build canoes, to transport and erect statues, and to burn; and probably as the native birds died out that had pollinated the trees’ flowers and dispersed their fruit. The destruction of the island’s animals was as extreme as that of the forest: without exception, every species of native land bird became extinct. The colonies of more than half of the seabird species breeding on Easter or on its offshore islets were wiped out. -- Jared Diamond
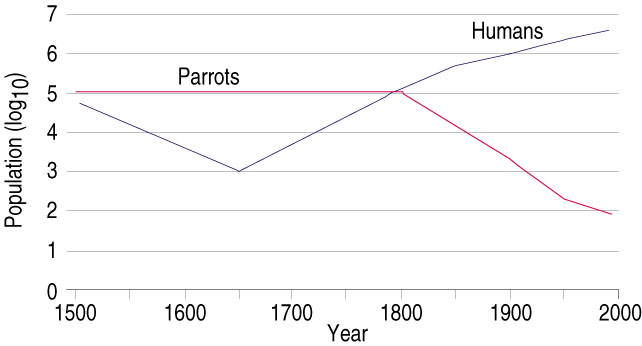
| Study
helps explain island populations' susceptibility to exotic diseases - Lindström et al. (2004) have found that Darwin's finches on smaller
islands in the Galapagos archipelago have weaker immune responses to disease
and foreign pathogens—findings that could help explain why island populations
worldwide are particularly susceptible to disease. Johannes Foufopoulos,
one of the co-authors, noted that "The introduction of exotic parasites
and diseases through travel, commerce and domestic animals and the resulting
destruction in native wildlife populations is a worldwide problem, but
it's even more serious for species that have evolved on islands. For example,
in the Hawaiian islands, many native bird species have gone extinct after
the introduction of avian malaria. The Galapagos authorities are now realizing
that the greatest danger to the islands' wildlife comes from exotic species,
such as invasive pathogens, accidentally introduced by humans." The investigators
found that larger islands with larger bird populations harbor more native
parasites and diseases, because the number of parasites is directly dependent
on the size of the population. Island size and parasite richness then influenced
the strength of the immune response of the hosts. By challenging the birds
immune systems with foreign proteins, they measured the average immune
response of each island population. Finches on smaller islands with fewer
parasites had a weaker immune response. For these birds, Foufopoulos said,
"maintaining a strong immune system is a little bit like house insurance:
you don't want to spend too much on an expensive policy if you live in
an area with no earthquakes, fires or floods." Similarly, if parasites
are scarce, the birds don't need to invest in an "expensive" immune system,
he said. When new parasites are then accidentally introduced by humans
to these islands, the birds are ill-prepared to resist infection.
See also: Darwin's Finches At Risk |
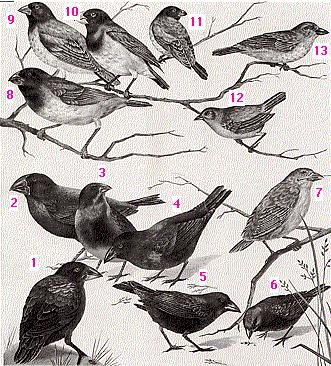
1. Large cactus finch (Geospiza conirostris), 2. Large ground finch (G. magnirostris), 3. Medium ground finch (Geospiza fortis), 4. Cactus finch (G. scandens), 5. Sharp-beaked ground finch (G. difficilis), 6. Small ground finch (G. fuliginosa), 7. Woodpecker finch (Cactospiza pallida), 8. Vegetarian tree finch (Platyspiza crassirostris), 9. Medium tree finch (Camarhynchus pauper), 10. Large tree finch (Camarhynchus psittacula), 11. Small tree finch (C. parvulus), 12. Warbler finch (Certhidia olivacea), and 13. Mangrove finch (Cactospiza heliobates) |
Recent changes in Bird Biogeography - Introductions:
Invasive species of birds
These introduced populations often thrive due to a lack of natural predators and abundant resources in suburban environments.
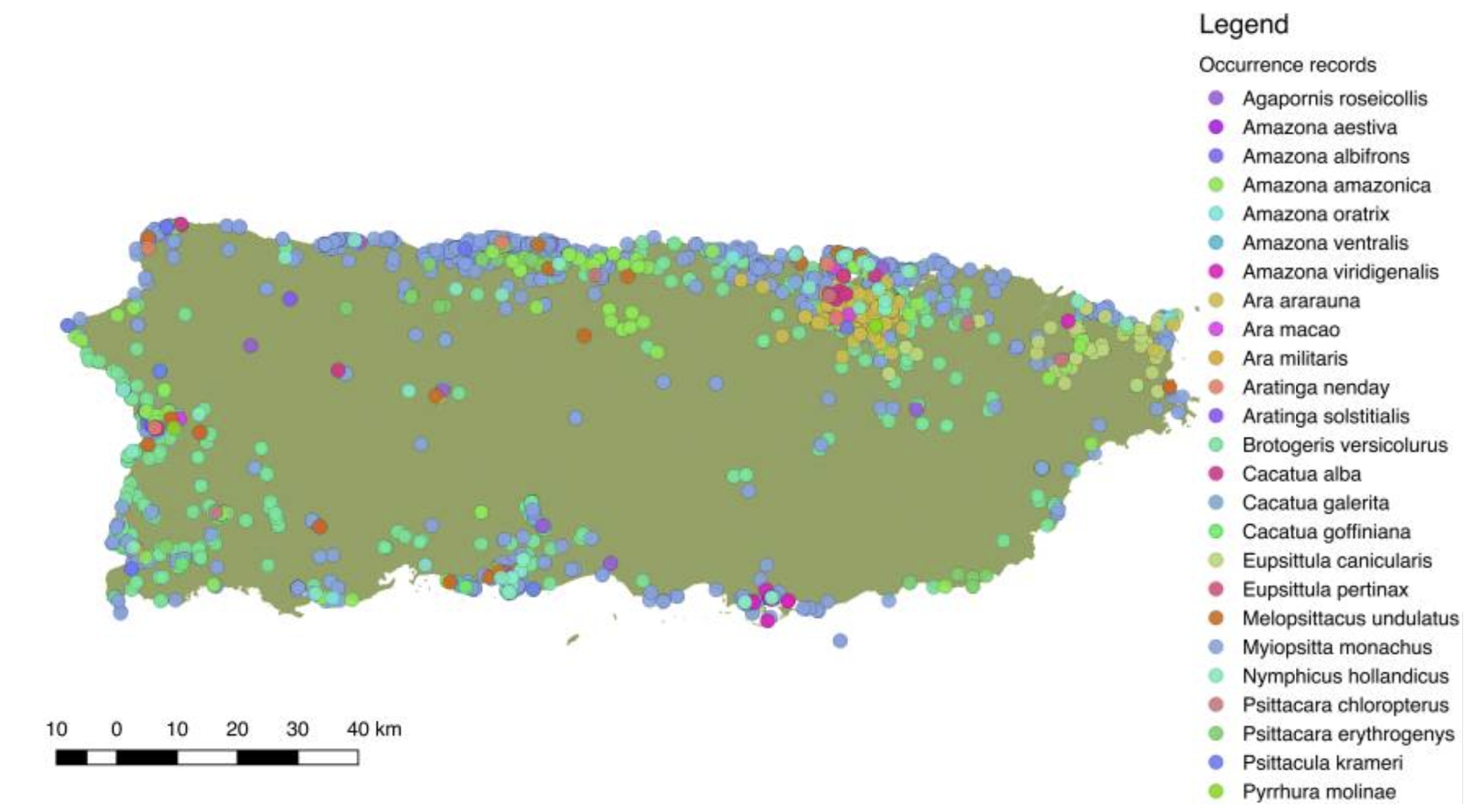
Distribution of 25 species of introduced Psittaciformes in Puerto Rico, depicted by the different colors. Sightings and reports
of Psittaciformes in Puerto Rico cover much of the island, but especially in coastal and highly (human) populated areas (From:
Falcón and Tremblay 2018).
Humans have been introducing non-native species of birds to new areas for centuries. For example, Ring-necked Pheasants (Phasianus colchicus), native to China and East Asian, were introduced into Europe by the ancient Greeks and Romans in about 1300 BC (Mason 1984). However, most introductions have occurred since the mid-1800s (Figure below). Cassey et al. (2015) noted two periods with accelerated rates of introductions, with the first extending from about 1800 to the early 1900s when Europeans colonized many new areas throughout the planet and introduced plants and animals from their former homelands for a number of reasons including nostalgia, aesthetics, and sport (Lever 1987). British colonists were particularly fond of introducing new species of birds, especially in Hawaii and other islands, New Zealand, Australia, and the continental United States (Blackburn et al. 2009). More than two-thirds of bird introductions during this period were on islands, primarily British colonies (Blackburn et al. 2009).
More than half of all introduced species of birds during this period were in the families Phasianidae (pheasants and quail), Anatidae (ducks, geese, and swans), Columbidae (pigeons and doves), Psittacidae (parrots), and Passeridae (Old World sparrows) (Lockwood 1999, Blackburn and Duncan 2001). In addition, the natural ranges of most introduced species during this period were in the Palearctic realm, eastern Africa, India, southeast Asia, and eastern Australia (Figure below). This period of accelerated rates of introductions ended by the early 1990s when it was finally recognized that introducing non-native species could have negative effects on native species and their habitats.
Unfortunately, non-native species continue to be introduced into new areas, but in more recent times the primary cause is the pet trade (Westphal et al. 2008). Birds kept as pets escape or owners tire of keeping them and deliberately release them. Most of these birds now come from South America, Africa, southeast Asia, and islands in the Pacific Ocean, particularly parrots (Psittaciformes), toucans (Piciformes), and songbirds (Passeriformes) from South America, parrots and songbirds from Africa, and babblers (Timalidae) and mynas (Sturnidae) from southeast Asia (Alves and Brooks 2010, Nijman 2010, Regueira and Bernard 2012). Many of these birds are captured in the wild for sale as pets, and many species, including several species of parrots, are now threatened or endangered as a result.
A number of investigators have attempted to evaluate the possible effects of introduced species of birds on native species (e.g., Evans et al. 2014, Baker et al. 2014, Martin-Albarracin et al. 2015). Overall, there is little evidence that introduced birds are a major threat to avian biodiversity globally (Evans et al. 2014). However, some introduced species have had a negative impact on some native species. Among the most important of those impacts is hybridization because hybridization contaminates native gene pools via genetic introgression and swamping. For example, non-native Mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) pose a threat by interbreeding with Pacific Black Ducks (A. superciliosa) and endangered Hawaiian Ducks (Anas wyvillliana), as do Ruddy Ducks (Oxyura jamaicensis) by interbreeding with endangered White-headed Ducks (O. leucocephala) (Baker et al. 2014; Figure below).
Introduced species can also have negative impacts on native species of birds via disease transmission. The introduction of two pathogens, Plasmodium relictum (avian malaria) and Avipoxvirus (avian pox), plus the introduction of mosquitoes that transmit the pathogens in about 1826 (Hardy 1960), are considered important factors in the declines in population and extinction of several species of birds in Hawaii (van Riper et al. 1986). Both diseases are thought to have been introduced in Hawaii within the past 150 years, but the exact dates and sites of introduction are unknown (Warner 1968, van Riper et al. 1986). Although the source(s) of these pathogens is(are) unknown, Atkinson and Lapointe (2009) suggested that they were likely introduced in the early 1900s when local bird clubs released several species of non-native songbirds from around the world to replace native birds whose populations were declining. From 1900 to the early 1960s, more than 50 species of non-native birds became established in Hawaii (Atkinson and Lapointe 2009).
Some introduced species impact native species by competing for nest sites, especially for cavity nest sites. Introduced species commonly cited as nest-site competitors include Crimson Rosellas (Platycercus elegans), Common Mynas (Acridotheres tristis), European Starlings (Sturnus vulgaris), and Rose-ringed Parakeets (Psittacula krameri) (Baker et al. 2014). Crimson Rosellas were introduced to Norfolk Island, a small island in the Pacific Ocean located between Australia, New Zealand, and New Caledonia, in the 1830s and has been reported to compete for nest cavities with two endangered species of endemic birds, Southern Boobooks (Ninox novaeseelandiae undulata) and Tasman Parakeets (Cyanoramphus cookii cookii) (Garnett et al. 2011). Similarly, endangered Seychelles Magpie-Robins (Copsycus sechellarum) have been negatively impacted by introduced Common Mynas. Interestingly, Common Mynas do not appear to interfere with the magpie-robins, but, when mynas being building nests in the same trees where the magpie-robins are nesting, the magpie-robins either abandon their nests or, if already incubating, spend much less time incubating, greatly reducing hatching success (Komdeur 1996). Non-native European Starlings also complete for nest cavities with many other species of cavity-nesting birds, but appear to have had limited or no effect on the population status of native cavity-nesters in North America (Koenig 2003). With few exceptions, e.g., Crimson Rosellas and Common Mynas, the same appears to be true for other introduced species that complete with native species for nest cavities (Baker et al. 2014).

Species richness of introduced species of birds based on 362 species of introduced birds with sufficient information to determine
their new ranges. Areas of particularly high species richness of introduced birds include Hawaii, southern California (CA),
southern Florida (FL), Taiwan, and New Zealand (NZ) (Figure modified a bit from Dyer et al. 2017).
Some species of birds threatened by extinction in their native ranges have been introduced and now have breeding populations elsewhere. For example, Yellow-crested Cockatoos (Cacatua sulphurea; Figure below) are critically endangered in their native range in eastern Indonesia and East Timor due to habitat loss and poaching for the pet trade. However, several decades ago, some of these cockatoos were released in Hong Kong and Singapore and both areas now have sizeable populations, with an estimated population of 200 in Hong Kong and a smaller, possibly declining population in Singapore (Neo 2012). Singapore is also home to more than 500 Red-breasted Parakeets (a near threatened species native to India and several countries in southeast Asia; Low and Owyong 2015) and more than 100,000 Javan Mynas (a vulnerable species native to Java and Bali; BirdLife International 2016). Such introduced populations could potentially be of value to conservation efforts, e.g., as surrogates for natural history studies, by providing an alternative source of birds for the pet trade and reducing demand for wild-caught birds, and as a source of birds for reintroduction programs (Figure below). However, conservationists would need to carefully consider the possible risk of increased demand that might result from harvesting birds from introduced populations as well as risks associated with using birds from introduced populations for reintroduction programs such as introducing diseases or parasites and (Gibson and Yong 2017).

Locations where threatened or endangered species of birds have been introduced and have establish breeding populations. Original locations:
1, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands; 2, northeast Mexico; 3, China; 4, Columbia, Guyana, Venezuela; 5, Indonesia; 6, Hispaniola;
7, Indonesia; 8, Indonesia; 9, Mexico; 10, Central America; 11, New Zealand (introduced on offshore islands); 12, French Polynesia (Rimatara, Kiribati).
CA, California; FL, Florida, NZ, New Zealand. Mariana Swiftlet, Aerodramus bartshi; Red-crowned Amazon, Amazona viridegenalis;
Reeve’s Pheasant, Syrmaticus reevesii; Red Siskin, Spinus cucullatus; Java Sparrow, Lonchura oryzivora; Hispaniolan Amazon, Amazona ventralis;
Javan Myna, Acridotheres javanicus; Yellow-crested Cockatoo, Cacatua sulphurea; Lilac-crowned Amazon, Amazona finschi;
Yellow-headed Amazon, Amazona oratrix; Weka, Gallirallus australis; Rimatara Lorikeet, Vini kuhlii (World map from Jenny and Patterson 2013; Data from Gibson and Yong 2017).
| Big brains & novel environments -- The widely held hypothesis that enlarged brains have evolved as an adaptation to cope with novel or altered environmental conditions lacks firm empirical support. Sol et al. (2005) tested this hypothesis for birds by examining whether large-brained species show higher survival than small-brained species when introduced to nonnative locations. Using a global database documenting the outcome of >600 introduction events, they confirmed that avian species with larger brains, relative to their body mass, tend to be more successful at establishing themselves in novel environments. Moreover, Sol et al. (2005) provided evidence that larger brains help birds respond to novel conditions by enhancing their innovation propensity rather than indirectly through noncognitive mechanisms. These findings provide strong evidence for the hypothesis that enlarged brains function, and hence may have evolved, to deal with changes in the environment. |
Recent changes in Bird Biogeography - Range Extensions and Shifts in Response to Climate Change:
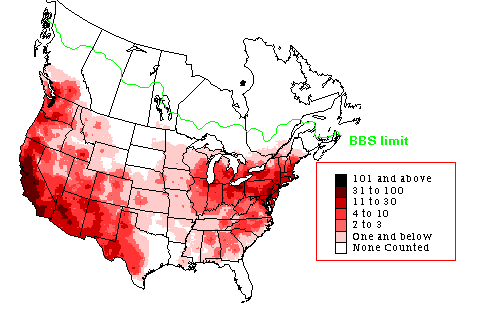
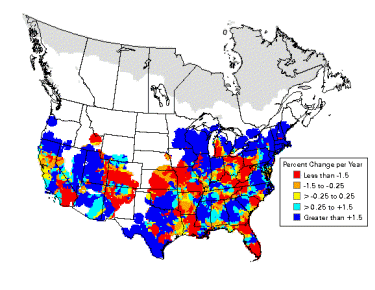 Blue-gray Gnatcatcher population trends (1966-2003). Note the increase in the northern portion of its breeding range. |
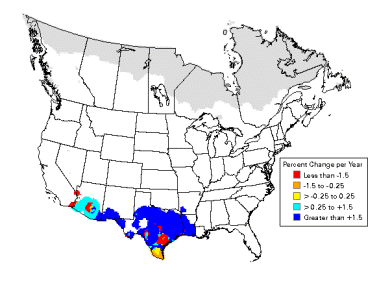 Inca Dove population trends (1966-2003). |
Breeding distributions of North American birds moving north -- Geographic changes in species distributions toward traditionally cooler climes is one hypothesized indicator of recent global climate change. Hitch and Leberg (2007) examined distribution data on 56 bird species. If global warming is affecting species distributions across the temperate northern hemisphere, data should show the same northward range expansions of birds that have been reported for Great Britain. Because a northward shift of distributions might be due to multidirectional range expansions for multiple species, the possibility that birds with northern distributions may be expanding their ranges southward was also examined. There was no southward expansion of birds with a northern distribution, indicating that there is no evidence of overall range expansion of insectivorous and granivorous birds in North America. As predicted, the northern limit of birds with a southern distribution showed a significant shift northward (2.35 km/year). Among the species showing the greatest shift northward were Inca Doves, Fish Crows, Blue-winged Warblers, Hooded Warblers, Blue-gray Gnatcatchers, Black-billed Cuckoos, and Golden-winged Warblers. This northward shift is similar to that observed in previous work conducted in Great Britain: the widespread nature of this shift in species distributions over two distinct geographical regions and its coincidence with a period of global warming suggests a connection with global climate change.
Migratory restlessness in a non-migratory bird - The urge of captive birds to migrate manifests itself in seasonally occurring restlessness, termed “Zugunruhe.” Key insights into migration and an endogenous basis of behavior are based on Zugunruhe of migrants but have scarcely been tested in nonmigratory birds. Helm and Gwinner (2006) recorded Zugunruhe in African Stonechats, small passerine birds that defend year-round territories and that diverged from northern migrants at least 1 million years ago. Such results demonstrate that Zugunruhe is a regular feature of their endogenous program, and is precisely timed by photoperiod. Such programs could be activated when movements by non-migratory birds become necessary. Helm and Gwinner (2006) propose that low-level Zugunruhe may be common in birds, including residents, and could underlie recent rapid changes in movement and range patterns attributed to global change and other human interventions. Attention to Zugunruhe of resident birds promises new insights into diverse and dynamic migration systems and enhances predictions of avian responses to global change.
Stonechats (Saxicola torquata) were ideal subjects for this study, with two subspecies: a north temperate migrant (S. t. rubicola) and an equatorial resident (S. t. axillaris). They display persistent circannual rhythms of molt and reproduction under constant conditions. Migrants show distinct Zugunruhe, timed by precise photoperiodic programs. In contrast to northern obligatory migrants, stonechats from equatorial Kenya defended their breeding territories throughout the year. Genetic distances between the two disjunctly distributed subspecies are large.
| Birds and Global Warming
Scientists of the U.S. Geological Survey, in cooperation with Canadian scientists, conduct the annual North American Breeding Bird Survey, which provides distribution and abundance information for birds across the United States and Canada. From these data, collected by volunteers under strict guidance from the U.S. Geological Survey, shifts in bird ranges and abundances can be examined. Because these censuses were begun in the 1960's, these data can provide a wealth of baseline information. Price (1995) has used these data to examine the birds that breed in the Great Plains. By using the present-day ranges and abundances for each of the species (e.g., Bobolink, top map on the right), Price derived large-scale, empiricalstatistical models based on various climate variables (for example, maximum temperature in the hottest month and total precipitation in the wettest month) that provided estimates of the current bird ranges and abundances (middle map on the right). Then, by using a general circulation model to forecast how doubling of CO2 would affect the climate variables in the models, he applied the statistical models to predict the possible shape and location of the birds' ranges and abundances (bottom map on the right). Significant changes were found for nearly all birds examined. The ranges of most species moved north, up mountain slopes, or both. The empirical models assume that these species are capable of moving into these more northerly areas, that is, if habitat is available and no major barriers exist. Such shifting of ranges and abundances could cause local extinctions in the more southern portions of the birds' ranges, and, if movement to the north is impossible, extinctions of entire species could occur. We must bear in mind, however, that this empiricalstatistical technique, which associates large-scale patterns of bird ranges with large-scale patterns of climate, does not explicitly represent the physical and biological mechanisms that could lead to changes in birds' ranges. Therefore, the detailed maps should be viewed only as illustrative of the potential for very significant shifts with different possible doubled CO2 climate change scenarios. Source: USGS |
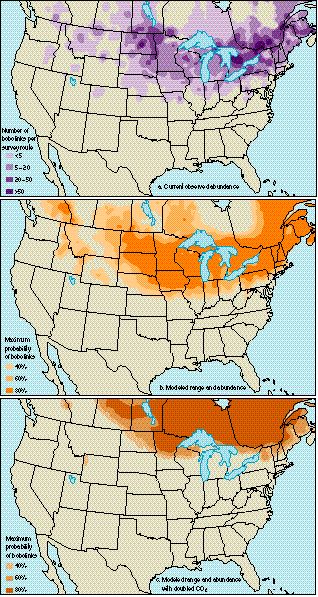
(a) Map of current range and abundance of the Bobolink as determined from actual observations during the U.S. Geological Survey Breeding Bird Survey and (b) map of current range and abundance of the bobolink as estimated from the empiricalstatistical model. The high correspondence in patterns between maps a and b suggests that this model reliably captures many of the features of the actual observed range and abundance of this species as depicted in map a. (c) Map of the forecasted range and abundance of the bobolink for climate change response of a model with doubled CO2. This map illustrates the potential for very significant shifts that doubled CO2 could cause (Price 1995). |
Climate change - birds nesting earlier
Climate change
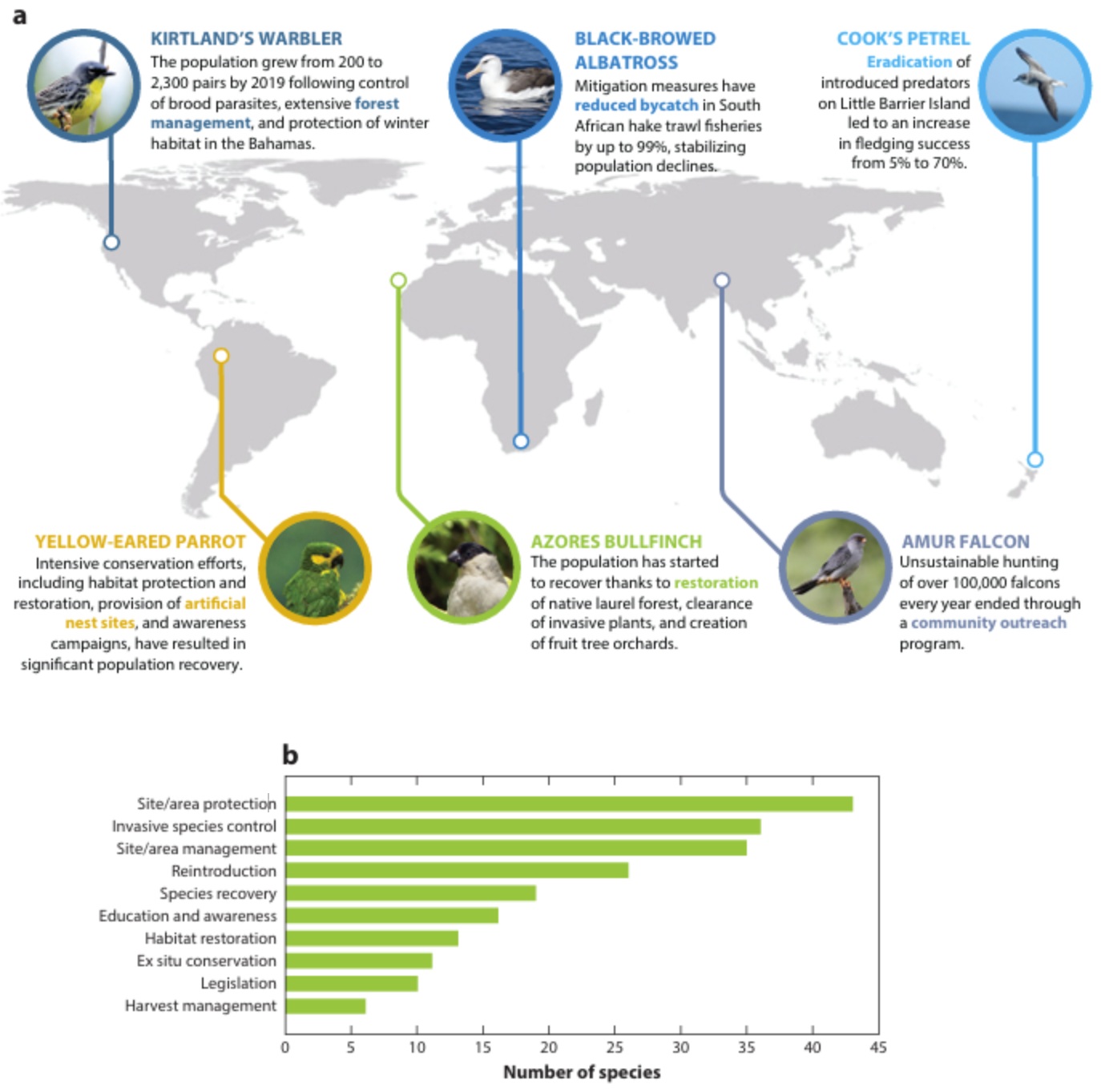
(a) Examples of successful bird conservation efforts. Key actions for each species are shown in colored, bold text.
(b) The top 10 actions implemented for species that have been downlisted on the IUCN Red List (From: Lees et al. 2022).
Literature cited
A.O.U. 1983. Check-list of North American birds, 6th ed. [with supplements through 1993]. American Ornithologists Union, Washington, DC.
Avise, J.C. 2000. Phylogeography: the history and formation of species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Avise, J.C. and D. Walker. 1998. Pleistocene phylogeographic effects on avian populations and the speciation process. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 265:457-463.
Baker, A.J. 1991. A review of New Zealand ornithology. Current Ornithology 8:1-67.
Brumfield, R. T., J. G. Tello, Z. A. Cheviron, M. D. Carling, and N. Crochet. 2007. Phylogenetic conservatism and antiquity of a tropical specialization: army-ant-following in the typical antbirds (Thamnophilidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 45:1-13.
Cerezer et al. 2022. Exceptions to the rule: Relative roles of time, diversification rates and regional energy in shaping the inverse latitudinal diversity gradient. Global Ecology and Biogeography 31: 1794-1809.
Cibois, A., B. Slikas, T. S. Schulenberg, and E. Pasquet. 2001. An endemic radiation of Malagasy songbirds is revealed by mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Evolution 55:1092-1206.
Cochran, W.W., H. Mouritsen, and M. Wikelski. 2004. Migrating songbirds recalibrate their magnetic compass daily from twilight cues. Science 304:405-408.
Cracraft, J. 1974. Continental drift and vertebrate distribution. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 5:215-261.
Darlington, P.J. 1957. Zoogeography: the geographical distribution of animals. J. Wiley and Sons, New York, NY.
Davies, R. G., C. D. L. Orme, D. Storch, V. A. Olson, G. H. Thomas, S. G. Ross, T.-S. Ding, P. C. Rasmussen, P. M. Bennett, I. P.F. Owens, T. M. Blackburn, and K. J. Gaston. 2007.Topography, energy and the global distribution of bird species richness. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 274: 1189=1197.
Falcón, W. and R. L Tremblay. 2018. From the cage to the wild: introductions of Psittaciformes to Puerto Rico. PeerJ 6:e5669.
Finn et al. 2023. More losers than winners: investigating Anthropocene defaunation through the diversity of population trends. Biological Reviews 98: 1732-1748.
Gaston, K.J., T. M. Blackburn, and K. K. Goldewijk. 2003. Habitat conversion and global avian biodiversity loss. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 270: 1293-1300.
Gill, F.B. 1995. Ornithology, second ed. W.H. Freeman and Co., New York, NY.
Hawkins, B. A., E. E. Porter, and J. A. F. Diniz-Filho. 2003. Productivity and history as predictors of the latitudinal diversity gradient of terrestrial birds. Ecology 84: 1608-1623.
Helm. B. and E. Gwinner. 2006. Migratory restlessness in an equatorial nonmigratory bird. PLoS Biol 4: e110.
Hitch, A. T. and P. L Leberg. 2007. Breeding distributions of North American bird species moving north as a result of climate change. Conservation Biology 21: 534-539.
Houde, P. and S.L. Olson. 1981. Paleognathous carinate birds from the early Tertiary of North America. Science 214:1236-1237.
Interiano et al. 2024. Interaction intensity as determinant of geographic range overlap between ant-following birds and army ants. Neotropical Biology and Conservation 19: 137-156.
Karr, J.R. 1990. Birds of tropical rainforest: comparative biogeography and ecology. Pp. 215-228 in Biogeography and ecology of forest bird communities (A. Keast, ed.). SPB Academic Publ., The Hague, Netherlands.
Klaassen, M. 1996. Metabolic constraints on long-distance migration in birds. Journal of Experimental Biology 199: 57-64.
Klicka, J. and R.M. Zink. 1997. The importance of recent Ice Ages in speciation: a failed paradigm. Science 277:1666-1669.
Lévêque et al. 2024. What passes through the extinction filter? Historical and contemporary patterns of vulnerability of the most extinction-prone bird family (Aves: Rallidae). Royal Society Open Science 8: 210262.
Lever, C. 1987. Naturalized birds of the world. Longman Scientific & Technical, Essex, England.
Lees et al. 2022. State of the World’s Birds. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 47:231–260.
Levey, D.J. and F.G. Stiles. 1992. Evolutionary precursors of long distance migration: resource availability and movement patterns in Neotropical landbirds. American Naturalist 140:447-476.
Lincoln, F. C., S. R. Peterson, and J. L. Zimmerman. 1998. Migration of birds. U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, D.C. Circular 16. Jamestown, ND: Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center Home Page. http://www.npwrc.usgs.gov/resource/othrdata/migratio/migratio.htm (Version 02APR2002).
Lindström, K.M., J. Foufopoulos, H. Pärn, & M. Wikelski. 2004. Immunological investments reflect parasite abundance in island populations of Darwin's finches. Proc. Roy. Soc. B 271:1513-1519.
Line, L. 2003. Silent spring: a sequel? National Wildlife, vol. 41.
Lovei, G.L. 1989. Passerine migration between the Palearctic and Africa. Current Ornithology 6:143-174.
MacArthur, R.H., H. Recher, & M.L. Cody. 1966. On the relation between habitat selection and species diversity. Am. Nat. 100:319-332.
MacArthur, R.H. and E.O. Wilson. 1967. The theory of island biogeography. Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, NJ.
Matthews et al. 2022. Threatened and extinct island endemic birds of the world: distribution, threats and functional diversity. Journal of Biogeography 49: 1920-1940.
Matthews et al. 2024. The global loss of avian functional and phylogenetic diversity from anthropogenic extinctions. Science 386:55–60.
Mayr, E. 1946. History of the North American bird fauna. Wilson Bulletin 58:3-41.
Mayr, E. 1964. Inference concerning the Tertiary American bird faunas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 51:280-288.
Mengel, R.N. 1964. The probable history of species formation in some northern wood warblers (Parulidae). Living Bird 3:9-43.
Moreau, R.E. 1952. Africa since the Mesozoic: with particular reference to certain biological problems. Proc. Zool. Soc. London 121:869-913.
Olson, S.L. 1985. The fossil record of birds. In D.S. Farner, J.R. King, and K.C. Parkes (eds.), Avian Biology, Vol. 8, pp. 79-238. Academic Press, New York.
Orme et al. 2006. Global Patterns of Geographic Range Size in Birds. PLoS Biology 4: e208.
Piersma, T., L. Zwarts, and J. H. Bruggeman. 1990. Behavioural aspects of the departure of waders before long-distance flights: flocking, vocalizations, flight paths and diurnal timing. Ardea 78: 157-184.
Popa-Lisseanu, A. G., A. Delgado-Huertas, M. G. Forero, A. Rodríguez, R. Arlettaz, and C. Ibáñezet. 2007. Bats' conquest of a formidable foraging niche: the myriads of nocturnally migrating songbirds. PLoS ONE 2: e205.
Porter, W. F.. 1994. Family Meleagrididae (Turkeys) in del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., & Sargatal, J., eds. Handbook of the Birds of the World, Vol. 2. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
Price, J. 1995. Potential impacts of global climate change on the summer distribution of some North American grasslands birds. Ph.D. dissertation, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI.
Proctor, N.S. and P.J. Lynch. 1993. Manual of ornithology: avian structure and function. Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, CN.
Rabenold, K.N. 1993. Latitudinal gradients in avian species diversity and the role of long-distance migration. Current Ornithology 10:247-274.
Rahbek, C. and G. R. Graves. 2001. Multiscale assessment of patterns of avian species richness. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 98:4534-4539.
Ramírez-Albores et al. 2021. Insights for protection of high species richness areas for the conservation of Mesoamerican endemic birds. Diversity and Distributions 27: 18-33.
Remsen, J. V., Jr. and T. A. Parker III. 1984. Arboreal dead-leaf-searching birds of the Neotropics. Condor 86:36-41.
Ribas, C. C., A. Aleixo, A. C. R. Nogueira, C. Y. Minaki, and J. Cracraft. 2012. A palaeobiogeographic model for biotic diversification within Amazonia over the past three million years. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 279: 681-689.
Sekercioglu, C. H., G. C. Daily, and P. R. Ehrlich. 2004. Ecosystem consequences of bird declines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101: 18042-18047.
Selander, R.K. 1971. Systematics and speciation in birds. Pp. 57-147 in Avian Biology, vol. 1 (D.S. Farner and J.R. King, eds.). Academic Press, New York, NY.
Sibley, C.G. and J.E. Ahlquist. 1985. The phylogeny and classification of the Australo-Papuan passerine birds. Emu 85:1-14.
Sol, D., R. P. Duncan, T. M. Blackburn, P. Cassey, and L. Lefebvre. 2005. Big brains, enhanced cognition, and response of birds to novel environments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 102: 5460-5465.
Weber, J.-M. 2009. The physiology of long-distance migration: extending the limits of endurance metabolism. Journal of Experimental Biology 212: 593-597.
Welty, J.C. and L. Baptista. 1988. The life of birds, 4th ed. Saunders College Publishing, New York, NY.
Wiens, J.A. 1991. Distribution. Pp. 156-174 in The Cambridge Encylopedia of Ornithology (M. Brooke and T. Birkhead, eds.). Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, NY.
Wiens, J. J. and M. J. Donoghue. 2004. Historical biogeography, ecology and species richness. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 19:639-644.
Wiles, G. J., J. Bart, R. E. Beck, and C. F. Aguon. 2003. Impacts of the Brown Tree Snake: patterns of decline and species persistence in Guam's avifauna. Conservation Biology 17: 1350-1360.
Willson, M.F. 1976. The breeding distribution of North American migrant birds: a critique of MacArthur (1959). Wilson Bulletin 88:582-587.